
Explain how you will convert a galvanometer into voltmeter.
Answer
522.2k+ views
Hint: First we know about galvanometer and voltmeter. A galvanometer is a device which is used to detect small electric current flowing in the circuit and Voltmeter is an instrument used to measure the potential difference across the two ends of a circuit element.
Complete step by step answer:
A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a large resistance in series to the galvanometer which is shown in diagram.
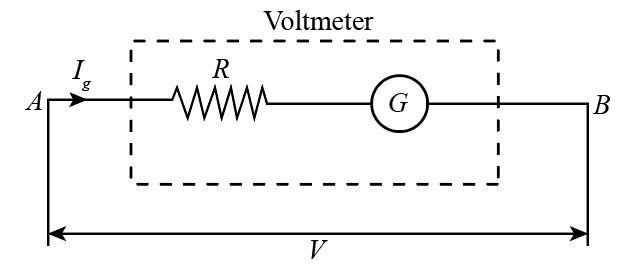
Let G and R be the resistance of a galvanometer and a conductor connected in series with it respectively.
Let V volt be the potential difference to be measured by the voltmeter and Ig, be the current.
Now potential difference between point A and B :
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_g}R + {I_g}G = {I_g}(R + G) \cr
& \cr
& \therefore R + G = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} \cr} $
$R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G$
This is the required value of resistance which must be connected in series to the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter of range 0-V volt.
Additional information: Voltmeter is a high resistance device. Resistance of an ideal voltmeter is infinite. A voltmeter is always connected in parallel to the circuit component across which voltage is to be measured.
Note: If we connect a simple galvanometer in parallel to the circuit, it will draw some current and hence the potential difference of the circuit will change and the measurement will not be accurate. For accurate measurement of the potential difference, it is essential that current between the two points should remain the same after connecting a measuring device. This is possible if the resistance of the device is infinite.
Complete step by step answer:
A galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a large resistance in series to the galvanometer which is shown in diagram.

Let G and R be the resistance of a galvanometer and a conductor connected in series with it respectively.
Let V volt be the potential difference to be measured by the voltmeter and Ig, be the current.
Now potential difference between point A and B :
$\eqalign{
& V = {I_g}R + {I_g}G = {I_g}(R + G) \cr
& \cr
& \therefore R + G = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} \cr} $
$R = \dfrac{V}{{{I_g}}} - G$
This is the required value of resistance which must be connected in series to the galvanometer to convert it into a voltmeter of range 0-V volt.
Additional information: Voltmeter is a high resistance device. Resistance of an ideal voltmeter is infinite. A voltmeter is always connected in parallel to the circuit component across which voltage is to be measured.
Note: If we connect a simple galvanometer in parallel to the circuit, it will draw some current and hence the potential difference of the circuit will change and the measurement will not be accurate. For accurate measurement of the potential difference, it is essential that current between the two points should remain the same after connecting a measuring device. This is possible if the resistance of the device is infinite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




