
Explain independent inheritance of two separate traits, i.e., shape and colour of seed (Round -Green RRyy and Wrinkled - yellow rrYY) Draw flow chart for \[F1\] and self-pollinated \[F2\] generation. Write the ratio.
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: In the field of genetics, Mendel laid the foundations and ultimately formulated the laws of inheritance. Gregor Mendel suggested three laws of inheritance: The Law of Segregation, the Law of Independent Assortment, and the Law of Dominance. His studies on pea plants with a range of traits resulted in these rules. Mendel used monohybrid crosses to investigate the inheritance of one gene in plants.
Complete answer:
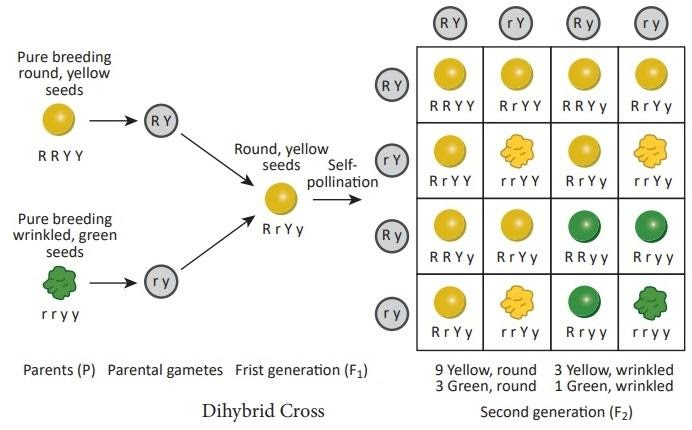
True-breeding lines of wrinkled yellow peas (rrYY) and round green peas form the P (Parental) cross (RRyy). As a result, all are RrYy alleles, these show round and yellow seeds. The alleles at the two loci segregate independently in the formation of \[F2\] plants. That is, the odds of having a R and a Y allele are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{2}$, a R and a y are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{2}$, and so on. As a result, all four potential diallelic combinations have a $\dfrac{1}{4}$ chance of occurring. Both parents are in the same boat. There are \[4 \times 4 = 16\] possible \[F2\] combinations given four possible gamete types in each parent, and the likelihood of any particular dihybrid form is $\dfrac{1}{4} \times \dfrac{1}{4} = \dfrac{1}{{16}}$.
That is, we expect round-yellow: wrinkled-yellow: round-green: wrinkled-green pea seeds to have a \[9:3:3:1\] phenotypic ratio.
Note:
A breeding experiment between two species that are similar hybrids for two traits is known as a dihybrid cross. A dihybrid cross, to put it another way, is a cross between two species that are heterozygous for two different traits. This type of trait has individuals that are homozygous for a particular trait. Genes, which are DNA segments, decide these characteristics.
In a dihybrid cross, each phenotype is represented by a separate pair of alleles carried by the parents. The dominant allele is carried by one parent, while the recessive allele is carried by the other. The \[F1\] generation's offspring are all heterozygous for particular traits as a result of the crosses.
Complete answer:
True-breeding lines of wrinkled yellow peas (rrYY) and round green peas form the P (Parental) cross (RRyy). As a result, all are RrYy alleles, these show round and yellow seeds. The alleles at the two loci segregate independently in the formation of \[F2\] plants. That is, the odds of having a R and a Y allele are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{2}$, a R and a y are $\dfrac{1}{2} \times \dfrac{1}{2}$, and so on. As a result, all four potential diallelic combinations have a $\dfrac{1}{4}$ chance of occurring. Both parents are in the same boat. There are \[4 \times 4 = 16\] possible \[F2\] combinations given four possible gamete types in each parent, and the likelihood of any particular dihybrid form is $\dfrac{1}{4} \times \dfrac{1}{4} = \dfrac{1}{{16}}$.
That is, we expect round-yellow: wrinkled-yellow: round-green: wrinkled-green pea seeds to have a \[9:3:3:1\] phenotypic ratio.

Note:
A breeding experiment between two species that are similar hybrids for two traits is known as a dihybrid cross. A dihybrid cross, to put it another way, is a cross between two species that are heterozygous for two different traits. This type of trait has individuals that are homozygous for a particular trait. Genes, which are DNA segments, decide these characteristics.
In a dihybrid cross, each phenotype is represented by a separate pair of alleles carried by the parents. The dominant allele is carried by one parent, while the recessive allele is carried by the other. The \[F1\] generation's offspring are all heterozygous for particular traits as a result of the crosses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




