
Explain Mendel’s mono hybridization experiment. Write the rules proposed on the basis of this experiment. Draw its diagram using Punnett square.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint:-Geneticists use the monohybrid cross to observe how homozygous descendants transmit heterozygous genotypes inherited from their ancestors. The inheritance of one gene is accountable for a monohybrid cross. It can be easily seen via Punnett Square.
Complete solution:-
A monohybrid cross is a genetic combination of homozygous genotypes between two individuals, resulting in a contrary phenotype. Mendel started with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting characteristics, i.e., one purple and one white, for the monohybrid cross. Plants with purple flowers were dominant plants that have resulted in the cross-pollination of purple and white flower plants. The hybrid plants were all purple. As the first hybrid generation (F1), he called this, and the offspring were called Filial1 or F1 progeny.
He performed an experiment with all seven contrasting pairs and found that one pattern in their behavior was exhibited by the entire F1 progeny, i.e., they resembled one of the parents. Fully missing was another parent character. He proceeded with his self-pollination experiment with F1 progeny plants. Surprisingly, one out of four plants had white flowers, while the other three were tall, he noted. The purple and white flower plants had a 3:1 ratio.
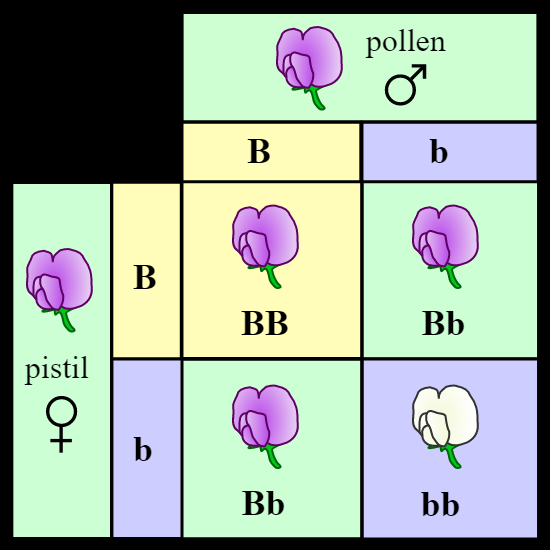
Note:- Gregor Johann Mendel, is known as the father and founder of genetics. The Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation, and Law of Independent Assortment are the three laws, known as Mendel’s laws of inheritance. These laws are based on the following four basic concepts:
● In more than one type of an allele, a gene does exist.
● The allelic pairs split when meiosis produces gametes, resulting in each gamete with a single allele.
● For each trait, every organism inherits two alleles.
● A pair’s two alleles are separate, i.e., one is dominant and the other is recessive.
Complete solution:-
A monohybrid cross is a genetic combination of homozygous genotypes between two individuals, resulting in a contrary phenotype. Mendel started with a pair of pea plants with two contrasting characteristics, i.e., one purple and one white, for the monohybrid cross. Plants with purple flowers were dominant plants that have resulted in the cross-pollination of purple and white flower plants. The hybrid plants were all purple. As the first hybrid generation (F1), he called this, and the offspring were called Filial1 or F1 progeny.
He performed an experiment with all seven contrasting pairs and found that one pattern in their behavior was exhibited by the entire F1 progeny, i.e., they resembled one of the parents. Fully missing was another parent character. He proceeded with his self-pollination experiment with F1 progeny plants. Surprisingly, one out of four plants had white flowers, while the other three were tall, he noted. The purple and white flower plants had a 3:1 ratio.

Note:- Gregor Johann Mendel, is known as the father and founder of genetics. The Law of Dominance, Law of Segregation, and Law of Independent Assortment are the three laws, known as Mendel’s laws of inheritance. These laws are based on the following four basic concepts:
● In more than one type of an allele, a gene does exist.
● The allelic pairs split when meiosis produces gametes, resulting in each gamete with a single allele.
● For each trait, every organism inherits two alleles.
● A pair’s two alleles are separate, i.e., one is dominant and the other is recessive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




