
Explain Monohybrid cross with suitable example.
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Mono means ‘one’ and hybrid means production of genetically mixed offspring.
Cross in which we study inheritance of one gene means to say the study of inheritance of one pair of contrasting characters is known as monohybrid cross.
Complete Answer:
We know that the Austrain monk Gregor Johann Mendel was first to explain the mechanism involved in the transmission of characters from parents to the offspring generation after generation.
- He started his Experiments with garden pea ‘Pisum sativum’.
- Mendel studied the inheritance of seven different pairs of contrasting characters in garden pea plants such as stem length, flower position, pod shape, pod colour, seed shape, seed colour, seed coat colour.
- A breeding experiment dealing with a single character is called a monohybrid cross.
Examples – height of plant, seed colour in pea, coat colour in guinea pig etc.
- Here we explain Mendel's famous experiment about the height of plants.
Explanation:
- In his experiment Mendel by transferring the pollens from tall (pure) to the stigma of dwarf plants (pure) and when the seeds matured he showed them and found that all the plants were tall. They constituted the f1 generation.
- These f1 plants were self pollinated and the seeds produced by all f1 plants were again collected and plants grown from them. These plants constituted the f2 generation. The plants of f2 generation were both tall and dwarf in approximate 3:1 ratio.
It means f2 generation consisted of three type of plants:
1) Tall homozygous means pure (alleles are Identical) 25%
2) Tall heterozygous means impure (both alleles are present) 50%
3) Dwarf homozygous means pure (alleles are Identical) 25%
- Tallness and dwarfness are regulated by a pair of contrasting factors (genes). A plant is tall because it possesses a factor for tallness t and a plant is dwarf because it has a factor for dwarfness t.
- These factors occur in pairs and are received one from either parent.
- Mendel cross pollinated a pure tall pea plant and a pure dwarf pea plant where tall pea plant genotype is tt and dwarf pea plant genotype is tt. During formation of gametes only one allele is present in each gamete so when these gametes cross and produce f1 generation shows tt genotype and in phenotype expression show tallness.
- When f1 plants were self pollinated where two types of gametes are produced in which one has t and other t. These gametes when cross produced both tall and dwarf pea plant genotypes such as tt, tt and tt in 1:2:1 ratio of genotype and 3:1 phenotype.
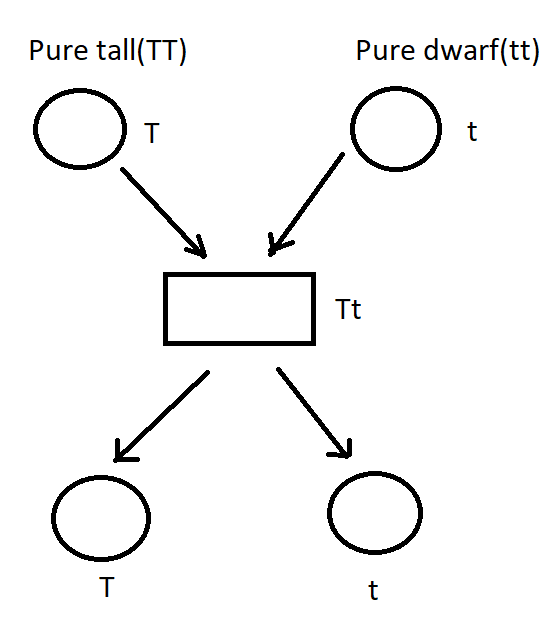
Punnett square:
Pure Tall: Hybrid Tall: Pure Dwarf
1 : 2 : 1
Tall pea plant: 1
Heterozygous tall pea plant: 2
Pure dwarf: 1
Note: Monohybrid cross is generally used to determine the dominance recessive relationship between two alleles. It also allows scientists to evaluate how heterozygous offspring express the genes they inherit.
Cross in which we study inheritance of one gene means to say the study of inheritance of one pair of contrasting characters is known as monohybrid cross.
Complete Answer:
We know that the Austrain monk Gregor Johann Mendel was first to explain the mechanism involved in the transmission of characters from parents to the offspring generation after generation.
- He started his Experiments with garden pea ‘Pisum sativum’.
- Mendel studied the inheritance of seven different pairs of contrasting characters in garden pea plants such as stem length, flower position, pod shape, pod colour, seed shape, seed colour, seed coat colour.
- A breeding experiment dealing with a single character is called a monohybrid cross.
Examples – height of plant, seed colour in pea, coat colour in guinea pig etc.
- Here we explain Mendel's famous experiment about the height of plants.
Explanation:
- In his experiment Mendel by transferring the pollens from tall (pure) to the stigma of dwarf plants (pure) and when the seeds matured he showed them and found that all the plants were tall. They constituted the f1 generation.
- These f1 plants were self pollinated and the seeds produced by all f1 plants were again collected and plants grown from them. These plants constituted the f2 generation. The plants of f2 generation were both tall and dwarf in approximate 3:1 ratio.
It means f2 generation consisted of three type of plants:
1) Tall homozygous means pure (alleles are Identical) 25%
2) Tall heterozygous means impure (both alleles are present) 50%
3) Dwarf homozygous means pure (alleles are Identical) 25%
- Tallness and dwarfness are regulated by a pair of contrasting factors (genes). A plant is tall because it possesses a factor for tallness t and a plant is dwarf because it has a factor for dwarfness t.
- These factors occur in pairs and are received one from either parent.
- Mendel cross pollinated a pure tall pea plant and a pure dwarf pea plant where tall pea plant genotype is tt and dwarf pea plant genotype is tt. During formation of gametes only one allele is present in each gamete so when these gametes cross and produce f1 generation shows tt genotype and in phenotype expression show tallness.
- When f1 plants were self pollinated where two types of gametes are produced in which one has t and other t. These gametes when cross produced both tall and dwarf pea plant genotypes such as tt, tt and tt in 1:2:1 ratio of genotype and 3:1 phenotype.

Punnett square:
| T | t | |
| T | TT(Tall) | Tt(Tall) |
| t | Tt(Tall) | tt(Dwarf) |
Pure Tall: Hybrid Tall: Pure Dwarf
1 : 2 : 1
Tall pea plant: 1
Heterozygous tall pea plant: 2
Pure dwarf: 1
Note: Monohybrid cross is generally used to determine the dominance recessive relationship between two alleles. It also allows scientists to evaluate how heterozygous offspring express the genes they inherit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




