
Explain nucleophilic substitution of alkyl halides?
Answer
495.6k+ views
Hint: Alkyl halides are the chemical compounds that are consisting of alkyl groups bonded to the halogen atom. Due to the polarity halogen group can be displaced by the nucleophiles like hydroxide and undergoes a nucleophilic substitution which are of two types namely unimolecular and bi-molecular substitution reactions.
Complete answer:
Halogen atoms are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. These are non-metals and has high electronegativity values. When alkyl groups are bonded with these halogens. The compounds were named as alkyl halides.
Due to the difference in the electronegativity and polarity between the alkyl groups and halogen atoms. Halogen atoms can be displaced by other nucleophiles like hydroxide in two ways.
One is \[S{N^1}\] which can be known as a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. It can take place in two steps. One step is generation of carbocation and the second step is attacking nucleophiles on carbocation. Tertiary alkyl halide undergoes this type of mechanism. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and primary carbocations.
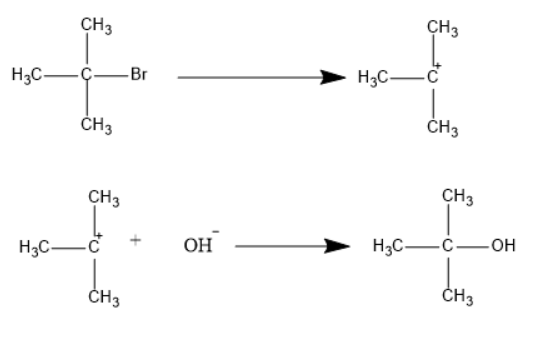
Another type is \[S{N^2}\] which can be known as bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. It can take place in single steps. Transition state will be formed in this reaction that leads to the inversion configuration of the product. Primary alkyl halides undergo this type of mechanism.
Note:
Mostly tertiary alkyl halides undergo unimolecular nucleophilic substitution as the tertiary carbocation is more stable. Primary alkyl halides undergo bimolecular nucleophilic substitution. Whereas secondary alkyl halides undergo both the mechanisms depending upon the conditions of chemical reaction.
Complete answer:
Halogen atoms are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine. These are non-metals and has high electronegativity values. When alkyl groups are bonded with these halogens. The compounds were named as alkyl halides.
Due to the difference in the electronegativity and polarity between the alkyl groups and halogen atoms. Halogen atoms can be displaced by other nucleophiles like hydroxide in two ways.
One is \[S{N^1}\] which can be known as a unimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. It can take place in two steps. One step is generation of carbocation and the second step is attacking nucleophiles on carbocation. Tertiary alkyl halide undergoes this type of mechanism. Tertiary carbocation is more stable than secondary and primary carbocations.

Another type is \[S{N^2}\] which can be known as bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction. It can take place in single steps. Transition state will be formed in this reaction that leads to the inversion configuration of the product. Primary alkyl halides undergo this type of mechanism.
Note:
Mostly tertiary alkyl halides undergo unimolecular nucleophilic substitution as the tertiary carbocation is more stable. Primary alkyl halides undergo bimolecular nucleophilic substitution. Whereas secondary alkyl halides undergo both the mechanisms depending upon the conditions of chemical reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




