
Explain the cleansing action of soaps.
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Soap molecules have hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts, so they get dissolved in respective mediums. They can form a round shaped body which can remove dirt.
Complete step by step answer:
Soaps also reduce the surface tension of the water and hence it gets easy for the water to reach most of the area of the clothes. This also helps in the cleansing process.
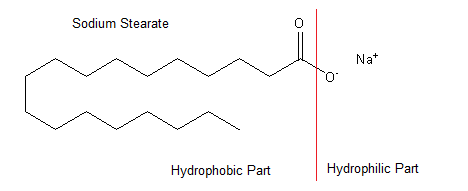
Below is the structure of sodium stearate which is a commonly used soap molecule.
Now we will see how a dirt particle or grease is removed by soap.
Hydrophobic tail of soap which is made up of a long alkyl chain, is soluble in grease or oil, hence it goes there when clothes are being washed and makes a large assembly of molecules around oily or greasy parts. Sometimes it is round in shape and sometimes when not possible, it gathers around in available space.
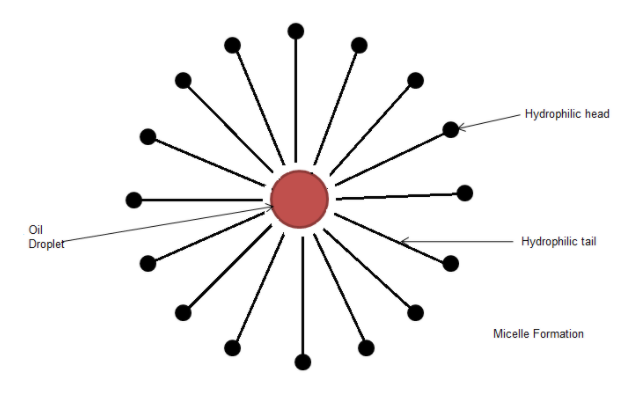
It is the round shaped assembly of soap molecules around an oil droplet. Hydrophobic part is on the inner side of the sphere and the hydrophilic part is on the outer side. This makes oily droplets separated from clothes and it becomes soluble in water as the outer part of micelle is hydrophilic. So, mechanical agitation starts this process and adding more water removes oil or grease from clothes.
Same mechanism is followed for dust particles and they are also removed from clothes by action of soaps.
Additional Information:
- We know that soap molecules are made up of two parts, hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head. Tail is generally made up of a long alkyl chain, hence it is not soluble in water, so it is hydrophobic. Head is made up of inorganic ions and it is very soluble in water, so it is a hydrophilic part.
- Lyophilic means that compound is not soluble in aqueous medium and lyophobic means compound is soluble in aqueous medium.
Note: - Remember that the hydrophobic part is not soluble in water and the hydrophilic part is always soluble in water.
Complete step by step answer:
Soaps also reduce the surface tension of the water and hence it gets easy for the water to reach most of the area of the clothes. This also helps in the cleansing process.
Below is the structure of sodium stearate which is a commonly used soap molecule.

Now we will see how a dirt particle or grease is removed by soap.
Hydrophobic tail of soap which is made up of a long alkyl chain, is soluble in grease or oil, hence it goes there when clothes are being washed and makes a large assembly of molecules around oily or greasy parts. Sometimes it is round in shape and sometimes when not possible, it gathers around in available space.

It is the round shaped assembly of soap molecules around an oil droplet. Hydrophobic part is on the inner side of the sphere and the hydrophilic part is on the outer side. This makes oily droplets separated from clothes and it becomes soluble in water as the outer part of micelle is hydrophilic. So, mechanical agitation starts this process and adding more water removes oil or grease from clothes.
Same mechanism is followed for dust particles and they are also removed from clothes by action of soaps.
Additional Information:
- We know that soap molecules are made up of two parts, hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head. Tail is generally made up of a long alkyl chain, hence it is not soluble in water, so it is hydrophobic. Head is made up of inorganic ions and it is very soluble in water, so it is a hydrophilic part.
- Lyophilic means that compound is not soluble in aqueous medium and lyophobic means compound is soluble in aqueous medium.
Note: - Remember that the hydrophobic part is not soluble in water and the hydrophilic part is always soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




