
Explain the construction and working of an electric bell with a figure.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: In this question we will study about the electric bell’s working and its construction with the help of diagrams. But firstly, we will understand about the electric bell and the concept behind it and hence this will help us a little more in approaching our answer.
Step-By-Step answer:
An electronic bell or a mechanical bell that works with the means of an electromagnet is known as an electric bell. Electric bells are generally used in schools, railroad crossings, fire, telephones, burglar alarms, alarms in industries, doorbells, etc. In an electric bell an electromagnet’s wire is insulated of coils or consists of coils wound round on iron rods.
An electric bell is constructed by the gong, a soft iron rod, an electromagnet and a contact screw. The electric bell is constructed by the iron core and one end of a coil (a wire) is connected to the terminal of the battery. When the hammer touches the screw, the steel rod acts like a spring and the hammer contacts the other terminal of the battery.
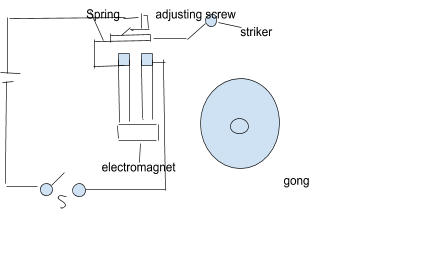
Working of the electric bell – Electric bell has electromagnet in it which has insulated wire coils wound round iron rods. Through the coils when electric current flows the magnetic field is created by the electromagnet which pulls the armature towards it which causes the hammer striking the bell. Hence, due to the flow of an electric current through the coils the rods become magnetic. The piece of an iron which is attached to the clapper attracts the rod. And when that clapper strikes the bell the bell rings.
NOTE: A repetitive buzzing or clanging sound is produced by the electric bell when the current is applied. When the current flows within the coil, a magnetic field is created by the electromagnetic which pulls the armature toward it due to which the hammer strikes the bell.
Step-By-Step answer:
An electronic bell or a mechanical bell that works with the means of an electromagnet is known as an electric bell. Electric bells are generally used in schools, railroad crossings, fire, telephones, burglar alarms, alarms in industries, doorbells, etc. In an electric bell an electromagnet’s wire is insulated of coils or consists of coils wound round on iron rods.
An electric bell is constructed by the gong, a soft iron rod, an electromagnet and a contact screw. The electric bell is constructed by the iron core and one end of a coil (a wire) is connected to the terminal of the battery. When the hammer touches the screw, the steel rod acts like a spring and the hammer contacts the other terminal of the battery.

Working of the electric bell – Electric bell has electromagnet in it which has insulated wire coils wound round iron rods. Through the coils when electric current flows the magnetic field is created by the electromagnet which pulls the armature towards it which causes the hammer striking the bell. Hence, due to the flow of an electric current through the coils the rods become magnetic. The piece of an iron which is attached to the clapper attracts the rod. And when that clapper strikes the bell the bell rings.
NOTE: A repetitive buzzing or clanging sound is produced by the electric bell when the current is applied. When the current flows within the coil, a magnetic field is created by the electromagnetic which pulls the armature toward it due to which the hammer strikes the bell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




