
Explain the construction of the meter bridge.
Answer
524.7k+ views
Hint: In order to give an answer to the question we will see what a meter bridge is and what it is used for and then we will know the construction of the meter bridge.
Complete answer:
The Slide Wire Bridge is another name for the metre bridge. It is made up of a one-meter-long wire with a uniform cross sectional area. The wire is now spread out over a metre scale. On either side of the cable, the bridge has two metallic strips in a reversed L form. The wire is held in place by these metallic strips. The strips are clamped to the wire. Metals such as copper are used to make these two metallic strips. The bridge is made up of a third metallic strip that is sandwiched between the first two, with a gap between them. On the bridge, there are a total of five leads.
As seen in the diagram, a resistance box R and an unknown resistance S are linked through the two gaps of the metallic strips. The middle lead of the metallic strip between the L shaped strips is attached to one end of the galvanometer. The galvanometer's other end is attached to a jockey. To slide on the bridge wire, the jockey is required. It's a metal rod with a knife edge on one end.
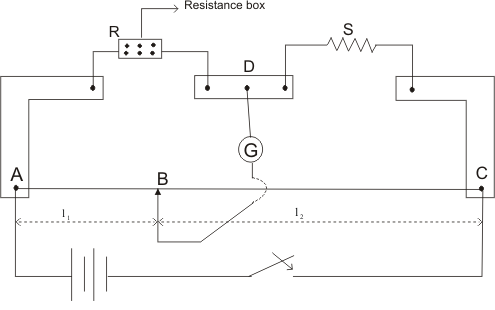
Now, in the resistance box, change the resistance value and slide the jockey along the cable. This procedure should be repeated until the galvanometer displays no or no deflection. Consider the galvanometer at point B, which showed no deflection. As a result, the jockey is now bound to the wire's point B. As a result, the distance between points A and B is calculated as L1 cm. The distance between points B and C is then L2 cm, which equals 100 - L1 cm. The metre bridge resembles the Wheatstone bridge now. For further clearance, the metre bridge has been redrawn as a Wheatstone bridge.
Note:
Note that while performing meter bridge practical in lab you will need the value of specific resistivity of the material of the wire, which is given as $\rho =\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}X}{L}$, where $r$ is that the radius of the wire, $X$ is the unknown resistance and $L$ is the length of the wire
Complete answer:
The Slide Wire Bridge is another name for the metre bridge. It is made up of a one-meter-long wire with a uniform cross sectional area. The wire is now spread out over a metre scale. On either side of the cable, the bridge has two metallic strips in a reversed L form. The wire is held in place by these metallic strips. The strips are clamped to the wire. Metals such as copper are used to make these two metallic strips. The bridge is made up of a third metallic strip that is sandwiched between the first two, with a gap between them. On the bridge, there are a total of five leads.
As seen in the diagram, a resistance box R and an unknown resistance S are linked through the two gaps of the metallic strips. The middle lead of the metallic strip between the L shaped strips is attached to one end of the galvanometer. The galvanometer's other end is attached to a jockey. To slide on the bridge wire, the jockey is required. It's a metal rod with a knife edge on one end.

Now, in the resistance box, change the resistance value and slide the jockey along the cable. This procedure should be repeated until the galvanometer displays no or no deflection. Consider the galvanometer at point B, which showed no deflection. As a result, the jockey is now bound to the wire's point B. As a result, the distance between points A and B is calculated as L1 cm. The distance between points B and C is then L2 cm, which equals 100 - L1 cm. The metre bridge resembles the Wheatstone bridge now. For further clearance, the metre bridge has been redrawn as a Wheatstone bridge.
Note:
Note that while performing meter bridge practical in lab you will need the value of specific resistivity of the material of the wire, which is given as $\rho =\dfrac{\pi {{r}^{2}}X}{L}$, where $r$ is that the radius of the wire, $X$ is the unknown resistance and $L$ is the length of the wire
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




