
Explain the Endoplasmic reticulum with its types and functions.
Answer
596.4k+ views
Hint: This organelle is an integral part of the endomembrane system suspended in the cytoplasm and aids in vesicular transport.
Complete answer:
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the largest single membrane-bound intracellular compartment. It is an extensive network of closed and flattened membrane-bound structures. The enclosed compartment is called the ER lumen. ER membranes are physiologically active, interact with the cytoskeleton, and contain differentiated domains specialized for distinct functions.
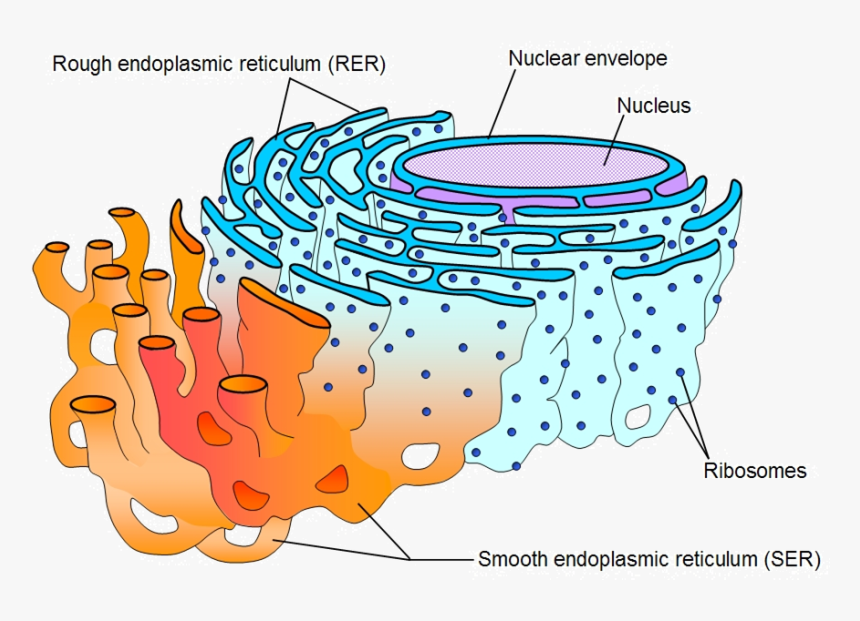
Fig: Endoplasmic reticulum
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
ER membranes are differentiated into rough and smooth regions (RER and SER, respectively), depending on whether ribosomes are associated with their cytoplasmic surfaces. Regions of ER that lack bound ribosomes are called SER (sometimes also called transition ER). The membranes and luminal spaces of the ER are normally continuous throughout the cell and that RER and SER form an interconnected membrane system.
Functions of Endoplasmic reticulum:
- Proteins synthesized by ribosomes associated with the membrane of RER enter the lumen and membrane of RER by the process of co-translational translocation.
- In the lumen of the RER, five principal modifications of proteins occur before they reach their final destinations: addition and processing of carbohydrates (N-linked glycosylation), the formation of disulfide bonds resulting in proper folding, specific proteolytic cleavages, and assembly into multimeric proteins.
- The SER acts as the site of lipid biosynthesis, detoxification, and calcium regulation.
Note: When cells are disrupted by homogenization, the ER breaks into fragments and reseals into small vesicles called microsomes. Microsomes derived from RER are studded with ribosomes on the outer surface and are called rough microsomes. Microsomes lacking attached ribosomes are called smooth microsomes.
Complete answer:
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the largest single membrane-bound intracellular compartment. It is an extensive network of closed and flattened membrane-bound structures. The enclosed compartment is called the ER lumen. ER membranes are physiologically active, interact with the cytoskeleton, and contain differentiated domains specialized for distinct functions.

Fig: Endoplasmic reticulum
Types of Endoplasmic Reticulum:
ER membranes are differentiated into rough and smooth regions (RER and SER, respectively), depending on whether ribosomes are associated with their cytoplasmic surfaces. Regions of ER that lack bound ribosomes are called SER (sometimes also called transition ER). The membranes and luminal spaces of the ER are normally continuous throughout the cell and that RER and SER form an interconnected membrane system.
Functions of Endoplasmic reticulum:
- Proteins synthesized by ribosomes associated with the membrane of RER enter the lumen and membrane of RER by the process of co-translational translocation.
- In the lumen of the RER, five principal modifications of proteins occur before they reach their final destinations: addition and processing of carbohydrates (N-linked glycosylation), the formation of disulfide bonds resulting in proper folding, specific proteolytic cleavages, and assembly into multimeric proteins.
- The SER acts as the site of lipid biosynthesis, detoxification, and calcium regulation.
Note: When cells are disrupted by homogenization, the ER breaks into fragments and reseals into small vesicles called microsomes. Microsomes derived from RER are studded with ribosomes on the outer surface and are called rough microsomes. Microsomes lacking attached ribosomes are called smooth microsomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




