
Explain the free radical mechanism of chlorination of methane.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: The chlorination of methane is performed under application of UV light. The reaction is used for the synthesis of chloroform and hexachlorobutadiene. It is performed by a free radical mechanism.
Step-By-Step answer:
The radical mechanism is characterised with three steps : chain initiation step, chain propagation step and chain propagation step. The chlorination reaction is as follows ;
$C{H_4} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + HCl$
Lets understand the mechanism of reaction,$C{H_4} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + HCl$
1. Chain initiation step – The first step of chlorination reaction is generation of an odd electron species. A chlorine molecule absorbs a photon and gives two chlorine radicals.
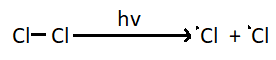
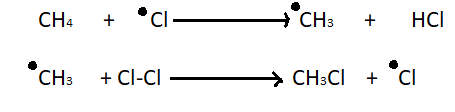
2. Chain propagation step - In chain propagation step a hydrogen atom leaves methane and it becomes a primary methyl radical. Then methyl radical results in the desired product and one more chlorine radical. This chlorine radical will go on to take part in another propagation reaction which results in a chain reaction.
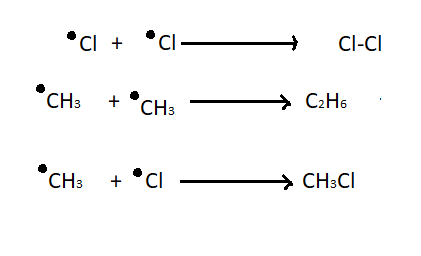
3. Chain termination step - This is the last step of chlorination of methane where recombination of two free radicals takes place. The termination step results in impurity in the final mixture.
Note: The first chain initiation step is endothermic, it takes heat approximately $2$ kcal per mole while the second step is exothermic and this step occurs very quickly. The chlorination of methane does not stop after one chlorination. It is very hard to get a monosubstituted chloromethane. To avoid this problem much higher concentration of methane should be taken in comparison to chlorine. This reduces the chances of a chlorine free radical to start a reaction again and again.
Step-By-Step answer:
The radical mechanism is characterised with three steps : chain initiation step, chain propagation step and chain propagation step. The chlorination reaction is as follows ;
$C{H_4} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + HCl$
Lets understand the mechanism of reaction,$C{H_4} + C{l_2} \to C{H_3}Cl + HCl$
1. Chain initiation step – The first step of chlorination reaction is generation of an odd electron species. A chlorine molecule absorbs a photon and gives two chlorine radicals.
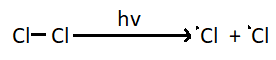
2. Chain propagation step - In chain propagation step a hydrogen atom leaves methane and it becomes a primary methyl radical. Then methyl radical results in the desired product and one more chlorine radical. This chlorine radical will go on to take part in another propagation reaction which results in a chain reaction.

3. Chain termination step - This is the last step of chlorination of methane where recombination of two free radicals takes place. The termination step results in impurity in the final mixture.

Note: The first chain initiation step is endothermic, it takes heat approximately $2$ kcal per mole while the second step is exothermic and this step occurs very quickly. The chlorination of methane does not stop after one chlorination. It is very hard to get a monosubstituted chloromethane. To avoid this problem much higher concentration of methane should be taken in comparison to chlorine. This reduces the chances of a chlorine free radical to start a reaction again and again.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




