
Explain the Huckel rule with example.
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Huckel rule is used to determine whether a molecule is aromatic or not based on the number of $\pi $ electrons and the physical structure of the ring. Benzene is an example of an aromatic compound.
Complete step by step solution:
Erick Huckel was a German chemist and physicist who in 1931 proposed an algorithm along with other conditions on the structure of planar ring organic compounds to determine whether the compound is organic or not. It is primarily based on the number of $\pi $ electrons in the ring structured organic compound (generally electrons in one out of double bonds). This number should be a multiple of (4n+2), where n is any integer greater than or equal to zero. These electrons should be in conjugation and thus the charge can move across the ring. Let us check for benzene which is known as the aromatic compound. The structure is as follows:
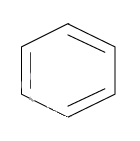
There are three $\pi $ bonds and thus total number of electrons = $3 \times 2 = 6$ which is a multiple of (4n+2) where n=1. So according to the Huckel rule, benzene is an aromatic compound. Now consider,
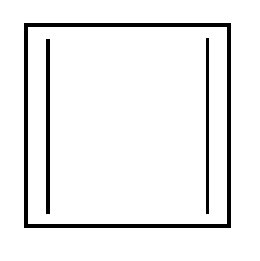
Cyclobutadiene. Here we have 2 $\pi $ bonds and thus total number of electrons = $2 \times 2 = 4$. If we equate it with 4n+2 then we get n=1/2 which is not an integer. Thus the above mentioned compound is not an aromatic compound.
Note: Huckel rule is not only about the formula but also planar structure of the molecule. If the ring does not form a plane then also the molecule loses its aromaticity. Even ionic compounds can be aromatic if the electrons are conjugated.
Complete step by step solution:
Erick Huckel was a German chemist and physicist who in 1931 proposed an algorithm along with other conditions on the structure of planar ring organic compounds to determine whether the compound is organic or not. It is primarily based on the number of $\pi $ electrons in the ring structured organic compound (generally electrons in one out of double bonds). This number should be a multiple of (4n+2), where n is any integer greater than or equal to zero. These electrons should be in conjugation and thus the charge can move across the ring. Let us check for benzene which is known as the aromatic compound. The structure is as follows:

There are three $\pi $ bonds and thus total number of electrons = $3 \times 2 = 6$ which is a multiple of (4n+2) where n=1. So according to the Huckel rule, benzene is an aromatic compound. Now consider,

Cyclobutadiene. Here we have 2 $\pi $ bonds and thus total number of electrons = $2 \times 2 = 4$. If we equate it with 4n+2 then we get n=1/2 which is not an integer. Thus the above mentioned compound is not an aromatic compound.
Note: Huckel rule is not only about the formula but also planar structure of the molecule. If the ring does not form a plane then also the molecule loses its aromaticity. Even ionic compounds can be aromatic if the electrons are conjugated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




