
Explain the importance of homologous organs in the process of evolution.
Answer
497.7k+ views
Hint: Homologous organs are considered to be evidence from comparative anatomy in the evolutionary process. If any similarity is found in organisms belonging to different groups, it is considered that there is a relationship between those organisms. These relationships can be understood from studying homologous structures.
Complete explanation:
Homologous organs are organs that are similar in structure but different in function. Let us consider the following example- forelimbs of man, cheetah, whale and bat. The forelimbs of the mentioned organisms possess similar anatomical structures and have similar bones. But, their function differs. The forelimb of a human is used to hold things, write; that of a cheetah is used to run and walk; a whale uses its forelimbs to swim and a bat uses its forelimbs to fly.
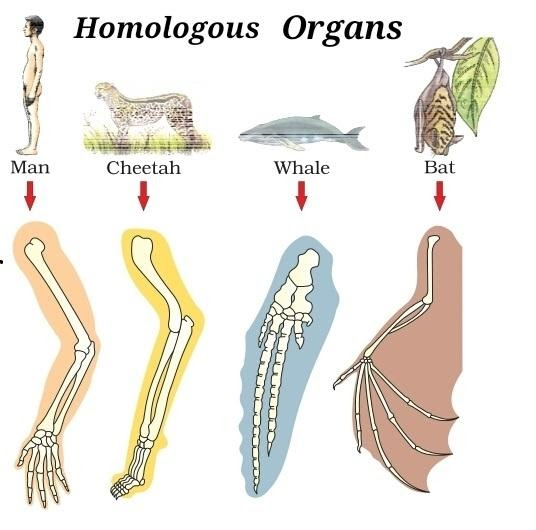
Homologous organs are an important example in the evolutionary process because it leads to divergent evolution. Organisms having homologous organs are thought to come from the same ancestor. These organs also help in knowing the phylogenetic relationship between different organisms.
Additional information:
Analogous organs are opposite of homologous organs. Analogous organs are organs that are different in structure but perform similar function. For example, wings of birds, bats and butterflies have different anatomical structures, but all perform the same function of flying.
Note:
The importance of homologous organs in the evolutionary process is to show the relationship between different organisms and prove they all had a common ancestor. The process through which interbreeding species split into two or more evolutionary groups is referred to as divergent evolution. Divergent evolution results from homologous organs.
Complete explanation:
Homologous organs are organs that are similar in structure but different in function. Let us consider the following example- forelimbs of man, cheetah, whale and bat. The forelimbs of the mentioned organisms possess similar anatomical structures and have similar bones. But, their function differs. The forelimb of a human is used to hold things, write; that of a cheetah is used to run and walk; a whale uses its forelimbs to swim and a bat uses its forelimbs to fly.

Homologous organs are an important example in the evolutionary process because it leads to divergent evolution. Organisms having homologous organs are thought to come from the same ancestor. These organs also help in knowing the phylogenetic relationship between different organisms.
Additional information:
Analogous organs are opposite of homologous organs. Analogous organs are organs that are different in structure but perform similar function. For example, wings of birds, bats and butterflies have different anatomical structures, but all perform the same function of flying.
Note:
The importance of homologous organs in the evolutionary process is to show the relationship between different organisms and prove they all had a common ancestor. The process through which interbreeding species split into two or more evolutionary groups is referred to as divergent evolution. Divergent evolution results from homologous organs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




