
Explain the mechanism for nitration of benzene.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: In electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction, the benzene ring acts as a nucleophile. It donates a pair of pi electrons to suitable electrophile. In the next step, deprotonation occurs.
Complete Step by step answer: Explain the mechanism for nitration of benzene.
Benzene reacts with nitric acid and sulphuric acid to form nitrobenzene. It is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. One hydrogen atom of benzene ring is replaced with nitro group. Nitric acid reacts with sulphuric acid to form nitronium ions.
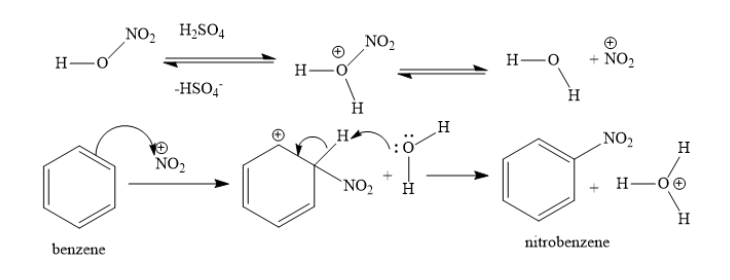
The pi electrons of benzene are donated to nitronium ions. A carbon-nitrogen bond is formed and the neighboring carbon atom gains unit positive charge. In this step, the aromaticity of the ring is broken. In the next step, this intermediate loses a proton to the water molecule. In this step, the aromaticity of the ring is regenerated.
Additional information: Some other examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction include sulphation, Friedel craft alkylation and Friedel craft acylation reactions.
Note: Aromatic compounds do not undergo addition reactions. Instead they undergo substitution reactions. If an additional reaction is carried out for the aromatic compounds, then the aromaticity of the benzene ring will be lost. This will decrease the stability. However, for substitution reactions, the aromaticity of benzene rings is restored. Hence, substitution is preferred over addition for aromatic compounds.
Complete Step by step answer: Explain the mechanism for nitration of benzene.
Benzene reacts with nitric acid and sulphuric acid to form nitrobenzene. It is an example of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. One hydrogen atom of benzene ring is replaced with nitro group. Nitric acid reacts with sulphuric acid to form nitronium ions.

The pi electrons of benzene are donated to nitronium ions. A carbon-nitrogen bond is formed and the neighboring carbon atom gains unit positive charge. In this step, the aromaticity of the ring is broken. In the next step, this intermediate loses a proton to the water molecule. In this step, the aromaticity of the ring is regenerated.
Additional information: Some other examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction include sulphation, Friedel craft alkylation and Friedel craft acylation reactions.
Note: Aromatic compounds do not undergo addition reactions. Instead they undergo substitution reactions. If an additional reaction is carried out for the aromatic compounds, then the aromaticity of the benzene ring will be lost. This will decrease the stability. However, for substitution reactions, the aromaticity of benzene rings is restored. Hence, substitution is preferred over addition for aromatic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




