
Explain the molecular orbital structure of benzene?
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: By using valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory first finds out all the required information and then find out the geometry of the required compound or molecule. Now we can find out the molecular orbital structure of benzene.
Complete step by step answer: Let us keenly observe the benzene ring, which shows that all carbon atoms in benzene are \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridized. The three \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals are lying in one plane and oriented at an angle of \[{{120}^{\circ }}\]. The fourth unhybridized p-orbital having two lobes is lying perpendicular to the plane of the hybrid orbital.
Two out of the three \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom overlap axially with \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals of the neighbouring carbon atoms on either side to form carbon-carbon sigma bonds. The third hybrid orbital of each carbon atom overlaps axially with the half-filled 1s- orbital of the hydrogen atom to form carbon-hydrogen sigma bonds.
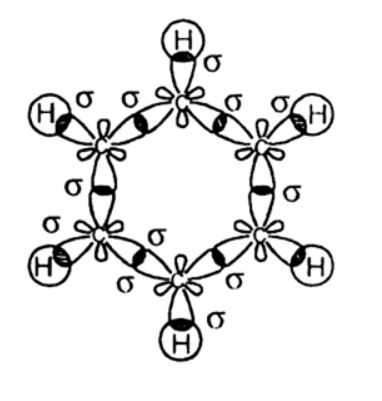
Thus, there are six sigma C-C bonds and six sigma C-H bonds. There is still one un-hybridized \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on each carbon atom. This orbital consists of two lobes, one lying above and the other below the plane of the ring.
The unhybridized \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on each carbon atom can overlap sidewise with the 2p,orbital of the two adjacent carbon atoms in two different ways as shown below giving rise to two sets of T bonds. Since \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on any carbon atom can overlap sideways with the \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on adjacent carbon atom on either side equally well, a continuous T-molecular 3 orbitals will result which embraces all the six p-electrons as shown:
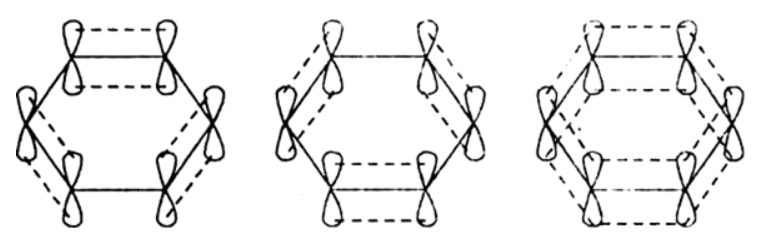
In benzene molecules all C-C-C and H-C-C are of \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] each and each C-C bond length is 139pm.
Note: Electronic configuration must follow Aufbau principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle and hands rule for arranging the electrons into their respective positions.
If we make a mistake finding a number of hybrid orbitals we will get the wrong conclusion.
Complete step by step answer: Let us keenly observe the benzene ring, which shows that all carbon atoms in benzene are \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybridized. The three \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals are lying in one plane and oriented at an angle of \[{{120}^{\circ }}\]. The fourth unhybridized p-orbital having two lobes is lying perpendicular to the plane of the hybrid orbital.
Two out of the three \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals of each carbon atom overlap axially with \[s{{p}^{2}}\] hybrid orbitals of the neighbouring carbon atoms on either side to form carbon-carbon sigma bonds. The third hybrid orbital of each carbon atom overlaps axially with the half-filled 1s- orbital of the hydrogen atom to form carbon-hydrogen sigma bonds.

Thus, there are six sigma C-C bonds and six sigma C-H bonds. There is still one un-hybridized \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on each carbon atom. This orbital consists of two lobes, one lying above and the other below the plane of the ring.
The unhybridized \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on each carbon atom can overlap sidewise with the 2p,orbital of the two adjacent carbon atoms in two different ways as shown below giving rise to two sets of T bonds. Since \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on any carbon atom can overlap sideways with the \[2{{p}_{z}}\] orbital on adjacent carbon atom on either side equally well, a continuous T-molecular 3 orbitals will result which embraces all the six p-electrons as shown:

In benzene molecules all C-C-C and H-C-C are of \[{{120}^{\circ }}\] each and each C-C bond length is 139pm.
Note: Electronic configuration must follow Aufbau principle, Pauli Exclusion Principle and hands rule for arranging the electrons into their respective positions.
If we make a mistake finding a number of hybrid orbitals we will get the wrong conclusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




