
Explain the nature of the image formed by the plane mirror.
Answer
509.4k+ views
Hint: The mirrors that have a flat reflecting surface are called plane mirrors. As we know light always reflects in a regular manner for a plane surface. We need to know certain rules to understand image formation by a plane mirror.
Complete answer:
Mirrors are a part of our daily lives. Is there any day you don’t look into the mirror? I doubt that very few answers would be no. But do you know how this image is formed? Well lets see how:
First thing to know is that images formed in the plane mirror are the same size as the object. The light ray coming from the object hits the plane mirror and reflects the ray back that forms an image. Now to have a better idea, let's learn the laws of reflection.
There are 2 laws of reflection:
1. The $1^{st}$ law states that the angle of the incident ray is equal to the angle of the reflected ray.
2. The normal, incident ray and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Look at the image below to get a better idea.
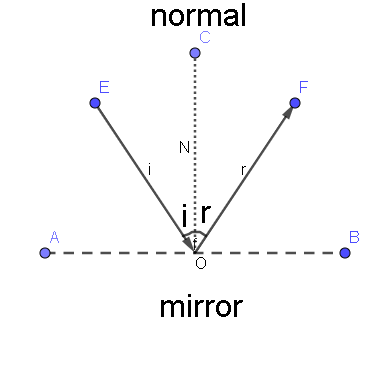
To understand how reflection is seen by us ,look at the following image:
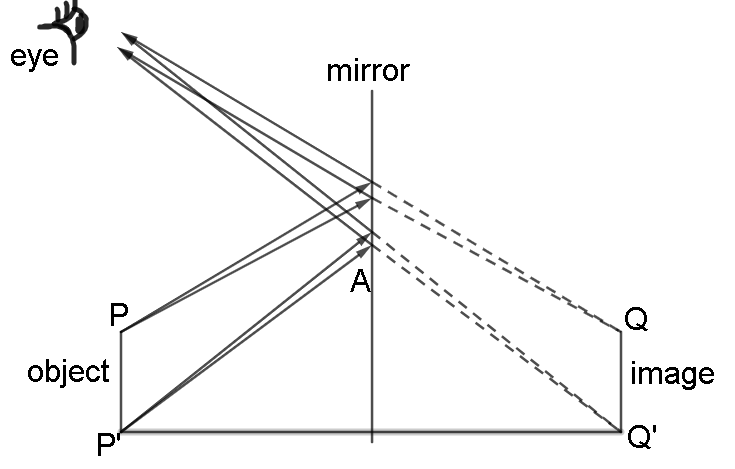
We see 2 rays emerging from the object , one from P and another from P’. They strike the mirror and reflect to our eyes . Here the law of reflection is applied to the trace path of the reflected ray. And if we further extend the rays backwards we see that the rays seem to originate from points Q and Q’. Thus if we go on making many such rays from the object we will see that the height of the object is equal to the height of the image.
And this is how image formation by a plane mirror takes place.
Note: Do not confuse between reflection and refraction. Laws are different for both cases. And also
Remember these points for convenience. The characteristic features of plane mirror are as follows:
The image formed is virtual and erect.
Image formed is equal to the size of the object.
Distance between object and mirror= distance between image and mirror
Image formed is behind the mirror.
Complete answer:
Mirrors are a part of our daily lives. Is there any day you don’t look into the mirror? I doubt that very few answers would be no. But do you know how this image is formed? Well lets see how:
First thing to know is that images formed in the plane mirror are the same size as the object. The light ray coming from the object hits the plane mirror and reflects the ray back that forms an image. Now to have a better idea, let's learn the laws of reflection.
There are 2 laws of reflection:
1. The $1^{st}$ law states that the angle of the incident ray is equal to the angle of the reflected ray.
2. The normal, incident ray and reflected ray all lie in the same plane.
Look at the image below to get a better idea.

To understand how reflection is seen by us ,look at the following image:

We see 2 rays emerging from the object , one from P and another from P’. They strike the mirror and reflect to our eyes . Here the law of reflection is applied to the trace path of the reflected ray. And if we further extend the rays backwards we see that the rays seem to originate from points Q and Q’. Thus if we go on making many such rays from the object we will see that the height of the object is equal to the height of the image.
And this is how image formation by a plane mirror takes place.
Note: Do not confuse between reflection and refraction. Laws are different for both cases. And also
Remember these points for convenience. The characteristic features of plane mirror are as follows:
The image formed is virtual and erect.
Image formed is equal to the size of the object.
Distance between object and mirror= distance between image and mirror
Image formed is behind the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




