
Explain the nucleophilic substitution reaction of chlorobenzene.
Answer
546k+ views
Hint: Chlorobenzene doesn’t give nucleophilic substitution reaction. But under very adverse conditions and specific reagents, chlorobenzene can give nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Complete answer:
We have studied about the basic named reactions as well as some of the related reactions in our chapters of chemistry.
Let us recollect these and approach the required answer.
Chlorobenzene is very less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. This is mainly because of two reasons:
- Resonance effect: Chlorine has a lone pair of electrons which are in conjugation with the π electrons of the benzene ring. This delocalisation of lone pairs of chlorine develops a partial double bond character in the C-Cl bond which makes it difficult for the nucleophile to cleave the C-Cl bond.
- Less polar C-Cl bond: The hybridisation of carbons in chlorobenzene is . carbons are more electronegative than the hybridised carbons. So, the carbons have a less tendency to release electrons to the chlorine atom. Thus, the C-Cl bond has less polarity, and hence less reactivity.
However, in some adverse conditions and reagents, chlorobenzene can give nucleophilic substitution reactions.
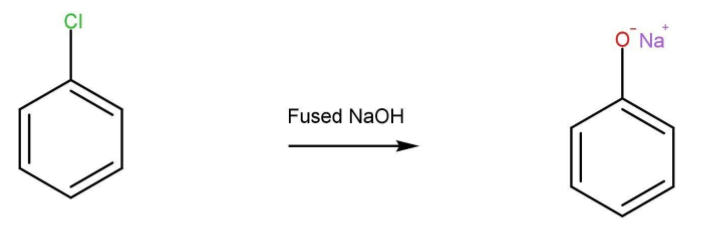
- Chlorobenzene when reacted with fused NaOH gives phenol. The reaction takes place at a high temperature. Phenol then again reacts with NaOH to give its salt.
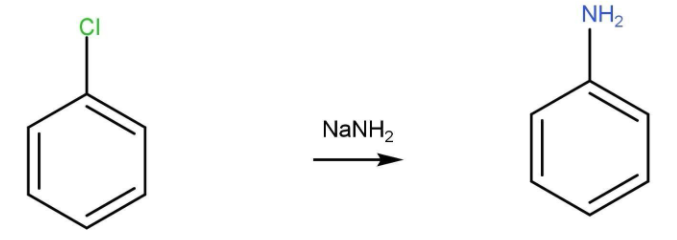
- Chlorobenzene reacts with sodium amide to give aniline.
Note:
Note that nucleophilic reactions are identified by the presence of both the electron pair donor and electron pair acceptor in the reaction and an $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised electrophile must have a leaving group in order for the reaction to take place.
Complete answer:
We have studied about the basic named reactions as well as some of the related reactions in our chapters of chemistry.
Let us recollect these and approach the required answer.
Chlorobenzene is very less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. This is mainly because of two reasons:
- Resonance effect: Chlorine has a lone pair of electrons which are in conjugation with the π electrons of the benzene ring. This delocalisation of lone pairs of chlorine develops a partial double bond character in the C-Cl bond which makes it difficult for the nucleophile to cleave the C-Cl bond.
- Less polar C-Cl bond: The hybridisation of carbons in chlorobenzene is . carbons are more electronegative than the hybridised carbons. So, the carbons have a less tendency to release electrons to the chlorine atom. Thus, the C-Cl bond has less polarity, and hence less reactivity.
However, in some adverse conditions and reagents, chlorobenzene can give nucleophilic substitution reactions.
- Chlorobenzene when reacted with fused NaOH gives phenol. The reaction takes place at a high temperature. Phenol then again reacts with NaOH to give its salt.

- Chlorobenzene reacts with sodium amide to give aniline.

Note:
Note that nucleophilic reactions are identified by the presence of both the electron pair donor and electron pair acceptor in the reaction and an $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised electrophile must have a leaving group in order for the reaction to take place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




