
Explain the physical phenomena involved in the formation of a rainbow with a diagram.
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: A rainbow is a multicolored circular arc usually seen after the rain when the Sun appears in the sky. Rainbow is always formed opposite to the Sun. Rainbows are formed due to the combined effect of three phenomena, namely, reflection, refraction, and dispersion of light.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us now discuss how the rainbow is formed. The condition for the formation of a rainbow is, presence of water droplets and while viewing it, Sun should be at your back.
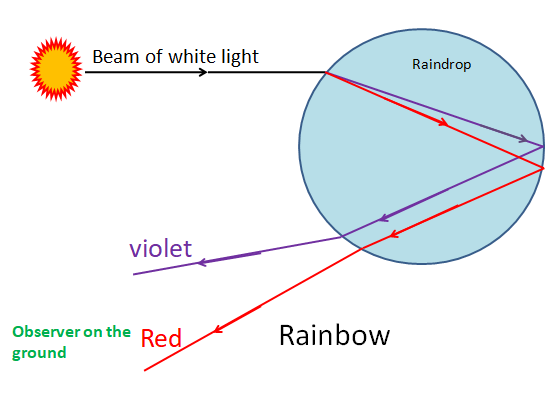
When Sun appears after the rain, the sunlight enters through the top of the water droplet by the refraction of light, the light entering the droplet splits into its components, then when it reaches the back of the droplet total internal reflection occurs.
The light reaches the top of the droplet, then it comes out by the process of refraction again. In this process, red light bends least and violet bends the maximum.
Following is the ray diagram showing the rainbow formation process.
Note:
To be able to see the rainbow, the viewing angle must be $40 - {42^o}$.
There are two types of Rainbows, primary and double rainbow. The primary rainbow is the one in which the red color is on the outer part of the arc and the violet color is on the inner side. A double rainbow is the one that has a secondary layer outside the primary layer and the colors are in reversed order, that is, red is on the inner side and violet is on the outer side.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us now discuss how the rainbow is formed. The condition for the formation of a rainbow is, presence of water droplets and while viewing it, Sun should be at your back.
When Sun appears after the rain, the sunlight enters through the top of the water droplet by the refraction of light, the light entering the droplet splits into its components, then when it reaches the back of the droplet total internal reflection occurs.
The light reaches the top of the droplet, then it comes out by the process of refraction again. In this process, red light bends least and violet bends the maximum.
Following is the ray diagram showing the rainbow formation process.

Note:
To be able to see the rainbow, the viewing angle must be $40 - {42^o}$.
There are two types of Rainbows, primary and double rainbow. The primary rainbow is the one in which the red color is on the outer part of the arc and the violet color is on the inner side. A double rainbow is the one that has a secondary layer outside the primary layer and the colors are in reversed order, that is, red is on the inner side and violet is on the outer side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




