
Explain the process of asexual reproduction in lower animals with the help of diagram.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint:
Asexual reproduction is the process of formation of daughter cell from specialized or unspecialized parts of a single parent without fertilization or fusion of gametes. Some methods of asexual reproduction is budding, fission, fragmentation, regeneration, spore formation and vegetative reproduction.
Complete answer:
In this question, we have asked about asexual reproduction. When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gamete formation is called asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction can be occur by following ways:
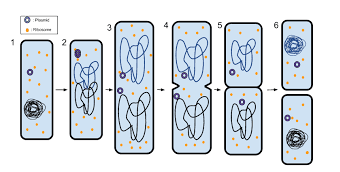
Fission: Amoeba reproduce by fission, in which an amoebic cell is simply divided into two identical cells. First, the nucleus divides and then the cells. This process is almost similar to mitosis.
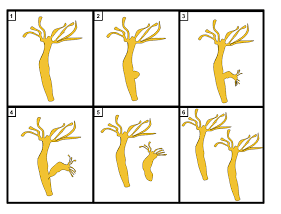
Budding: In budding, bud develops as an outgrowth due to many cell divisions at one site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and, when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals. Budding is seen in Hydra.
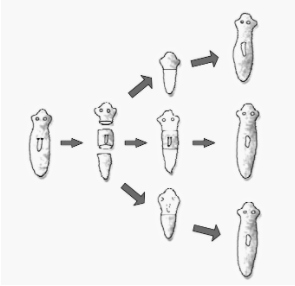
Fragmentation: In fragmentation, an organism is split into fragments. Each fragment develops into a matured organism, which is genetically and morphologically identical to their parents.
Regeneration: In regeneration, the organism is capable of regrowing its body parts and regeneration occurs via mitosis.
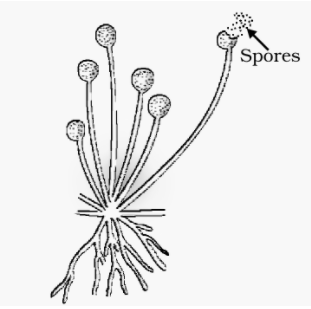
Spore formation: When spores land on food under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new plants.
Vegetative reproduction: Vegetative reproduction occurs in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant.

Note: By asexual reproduction, population increase rapidly and the exact copies of the parent is form which is called clone. By this way, we can restore the required characteristics of the organisms, which may be lost in sexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction is the process of formation of daughter cell from specialized or unspecialized parts of a single parent without fertilization or fusion of gametes. Some methods of asexual reproduction is budding, fission, fragmentation, regeneration, spore formation and vegetative reproduction.
Complete answer:
In this question, we have asked about asexual reproduction. When offspring is produced by a single parent with or without the involvement of gamete formation is called asexual reproduction.
Asexual reproduction can be occur by following ways:
Fission: Amoeba reproduce by fission, in which an amoebic cell is simply divided into two identical cells. First, the nucleus divides and then the cells. This process is almost similar to mitosis.

Budding: In budding, bud develops as an outgrowth due to many cell divisions at one site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and, when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals. Budding is seen in Hydra.

Fragmentation: In fragmentation, an organism is split into fragments. Each fragment develops into a matured organism, which is genetically and morphologically identical to their parents.
Regeneration: In regeneration, the organism is capable of regrowing its body parts and regeneration occurs via mitosis.

Spore formation: When spores land on food under favourable conditions, they germinate and produce new plants.

Vegetative reproduction: Vegetative reproduction occurs in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment of the parent plant.

Note: By asexual reproduction, population increase rapidly and the exact copies of the parent is form which is called clone. By this way, we can restore the required characteristics of the organisms, which may be lost in sexual reproduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




