
Explain the process of oogenesis in humans.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: In the human female reproductive system, a growth process takes place which is responsible for the development of the primary egg cell (or ovum) into a mature and functional ovum.
Complete answer:
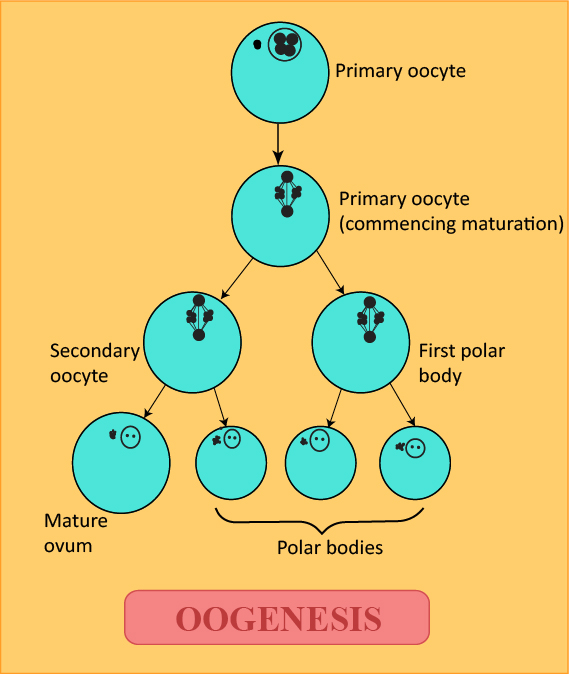
In the case of a woman, the egg’s development starts before the female that carries it is even born; 8 to 20 weeks after the fetus has started to grow, the cells that are to become mature ova start multiplying. By the time the female is born, all of the egg cells that the ovaries will release during the active reproductive years of the female are already present in the ovaries. These cells are known as the primary ova and are around 400,000 in number. The primary ova remains dormant until the ovulation when an egg is released from the ovary.
The egg then undergoes cell division. The nucleus splits such that half of its chromosomes go to one cell and a half to another. One of these two new cells is usually larger than the other and is known as the secondary ovum and the smaller cell is known as a polar body. The secondary ovum grows in the ovary until it reaches the maturation; it then breaks loose and is carried into the fallopian tubes. Once in the fallopian tubes, the secondary egg cell is now suitable for fertilization by the male sperm cells.
Some egg cells may not even mature for 40 years; others degenerate and never mature.
Note: Most women release an egg cell every menstrual cycle (vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman's monthly cycle), this is called ovulation. After 12-24 hours, the egg cell dies and it won’t be possible to become pregnant again until the next cycle.
Complete answer:
In the case of a woman, the egg’s development starts before the female that carries it is even born; 8 to 20 weeks after the fetus has started to grow, the cells that are to become mature ova start multiplying. By the time the female is born, all of the egg cells that the ovaries will release during the active reproductive years of the female are already present in the ovaries. These cells are known as the primary ova and are around 400,000 in number. The primary ova remains dormant until the ovulation when an egg is released from the ovary.
The egg then undergoes cell division. The nucleus splits such that half of its chromosomes go to one cell and a half to another. One of these two new cells is usually larger than the other and is known as the secondary ovum and the smaller cell is known as a polar body. The secondary ovum grows in the ovary until it reaches the maturation; it then breaks loose and is carried into the fallopian tubes. Once in the fallopian tubes, the secondary egg cell is now suitable for fertilization by the male sperm cells.
Some egg cells may not even mature for 40 years; others degenerate and never mature.

Note: Most women release an egg cell every menstrual cycle (vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman's monthly cycle), this is called ovulation. After 12-24 hours, the egg cell dies and it won’t be possible to become pregnant again until the next cycle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




