
Explain the structure of a Biogas plant.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Biogas plant is a dome like structure, in which different rooms are present like, mixing tank, inlet chamber, outlet chamber, one digester and overflow chamber.
Complete answer:
Biogas basically is a gaseous mixture of gases produced by fermentation of different organic matter which involve household waste, domestic waste, animal waste, etc. This gas mainly consists of methane which is a result of metabolism of microorganisms feeding on the organic waste. So, we develop different and effective structures for biogas production.
Now, Biogas plants are somewhat, like dome structures. These are made up of bricks and cement. This is a sample diagram of a Biogas plant.
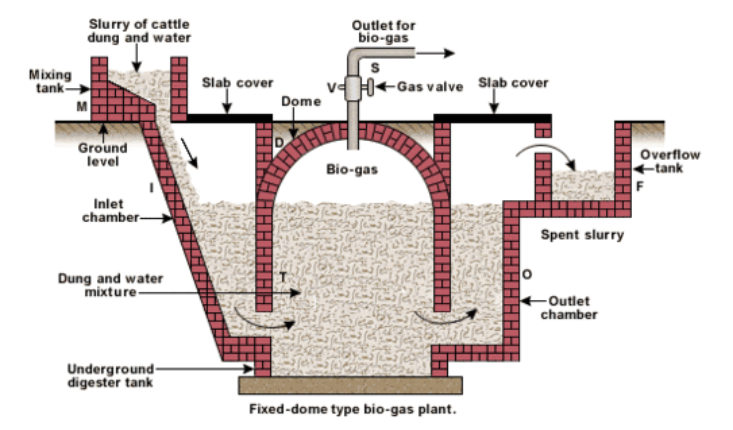
This plant consists of different chambers or rooms:
> Mixing tank – This tank is present above the ground where all waste is collected and everything collected is mixed to be processed further.
> Inlet chamber- This basically consists of two parts inlet pipe and storage place where inlet pipe will collect all the waste from mixing chamber.
> Digester- This tank is present underground so that proper anaerobic conditions can be provided to microbes to grow and to produce desired output. In this tank an outlet pipe is also connected which takes out gas which is produced inside.
> Outlet chamber – this tank is required to collect all dead biomass or remaining fragments of input waste. It took out all the waste from the digester.
> Overflow tank – Outlet chamber opens in a small overflow tank where all processed or waste material can be stored.
So, this was all about structure and a little bit about the function of each part of the Biogas plant.
Note: Biogas typically refers to a mixture of different gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Mixing tan and overflow chambers are present above the ground and digesters where microorganisms grow, are present deep inside the ground.
Complete answer:
Biogas basically is a gaseous mixture of gases produced by fermentation of different organic matter which involve household waste, domestic waste, animal waste, etc. This gas mainly consists of methane which is a result of metabolism of microorganisms feeding on the organic waste. So, we develop different and effective structures for biogas production.
Now, Biogas plants are somewhat, like dome structures. These are made up of bricks and cement. This is a sample diagram of a Biogas plant.

This plant consists of different chambers or rooms:
> Mixing tank – This tank is present above the ground where all waste is collected and everything collected is mixed to be processed further.
> Inlet chamber- This basically consists of two parts inlet pipe and storage place where inlet pipe will collect all the waste from mixing chamber.
> Digester- This tank is present underground so that proper anaerobic conditions can be provided to microbes to grow and to produce desired output. In this tank an outlet pipe is also connected which takes out gas which is produced inside.
> Outlet chamber – this tank is required to collect all dead biomass or remaining fragments of input waste. It took out all the waste from the digester.
> Overflow tank – Outlet chamber opens in a small overflow tank where all processed or waste material can be stored.
So, this was all about structure and a little bit about the function of each part of the Biogas plant.
Note: Biogas typically refers to a mixture of different gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. Mixing tan and overflow chambers are present above the ground and digesters where microorganisms grow, are present deep inside the ground.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




