
Explain the structure of megasporangium?
Answer
530k+ views
Hint: Megasporangia are female sporangia that produce megasporocytes that produce megaspores. The sporangia may be borne in specialized structures such as sori in ferns, cones in some pteridophytes and mostly found in gymnosperms or flowers in angiosperms.
Complete answer:
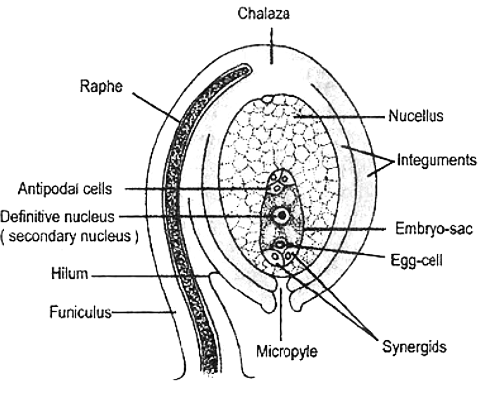
- Megasporangia arises from the placenta typically known as ovules.
- Ovules in an ovary may be one or many in number.
- For example Wheat, paddy and mango contains only one ovule.
- Water melon, Papaya and orchids contain many numbers of ovules.
- The megasporangium commonly known as ovule is a small structure which is attached to the placenta with the help of a stalk called funicle.
- The body of the ovule fuses with the funcle in a region called a hilum.
- Protective covering around an ovule is known as integument.
- Integuments consist of the nucleus except at the tip where a small opening called micropyle is organized.
- At the other end of the micropyle is chalaza which represents the basal part of ovule.
- Female gametophyte is also known as embryo sac and is present inside the nucellus.
- In megasporogenesis, the diploid megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form 4 haploid megaspores.
- Three out of four megaspores degenerate and only one is functional.
- The functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte.
- Female gametophyte is a 7 celled and 8 nucleated structure consisting of two synergies, three antipodal cells, two polar nuclei and 1 egg cell.
Additional information:
Stigma: It serves as the landing platform for pollen grains.
Style: It is the elongated slender part beneath the stigma.
Ovary: It is the basal swollen part of the pistil.
Inside the ovary we found an ovarian cavity also known as locule.
Note: Megasporangium is a sporangium which produces only megaspores. Ovule is the structure in a plant that develops into a seed after fertilization; the megasporangium of a seed plant with its enclosing integuments. Many found in gymnosperms and gymnosperms.
Complete answer:
- Megasporangia arises from the placenta typically known as ovules.
- Ovules in an ovary may be one or many in number.
- For example Wheat, paddy and mango contains only one ovule.
- Water melon, Papaya and orchids contain many numbers of ovules.
- The megasporangium commonly known as ovule is a small structure which is attached to the placenta with the help of a stalk called funicle.
- The body of the ovule fuses with the funcle in a region called a hilum.
- Protective covering around an ovule is known as integument.
- Integuments consist of the nucleus except at the tip where a small opening called micropyle is organized.
- At the other end of the micropyle is chalaza which represents the basal part of ovule.
- Female gametophyte is also known as embryo sac and is present inside the nucellus.
- In megasporogenesis, the diploid megaspore mother cell undergoes meiosis to form 4 haploid megaspores.
- Three out of four megaspores degenerate and only one is functional.
- The functional megaspore develops into the female gametophyte.
- Female gametophyte is a 7 celled and 8 nucleated structure consisting of two synergies, three antipodal cells, two polar nuclei and 1 egg cell.

Additional information:
Stigma: It serves as the landing platform for pollen grains.
Style: It is the elongated slender part beneath the stigma.
Ovary: It is the basal swollen part of the pistil.
Inside the ovary we found an ovarian cavity also known as locule.
Note: Megasporangium is a sporangium which produces only megaspores. Ovule is the structure in a plant that develops into a seed after fertilization; the megasporangium of a seed plant with its enclosing integuments. Many found in gymnosperms and gymnosperms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




