
Explain the structure of placenta. Also write two functions of placenta.
Answer
578.4k+ views
Hint: Placenta the unique organ is found only in mammals. It is the organ that helps in the transportation of the nutrients from the mother to the foetus. The nutrients are sent from the period between conceptions to birth.
Complete answer: The major function of the placenta is to provide nutrients to the foetus and develop the foetus. This is done in stages. First, the foetus gets attached to the uterine wall. It provides nutrients to the foetus and allows the foetus to transfer the waste material to the mother’s blood.
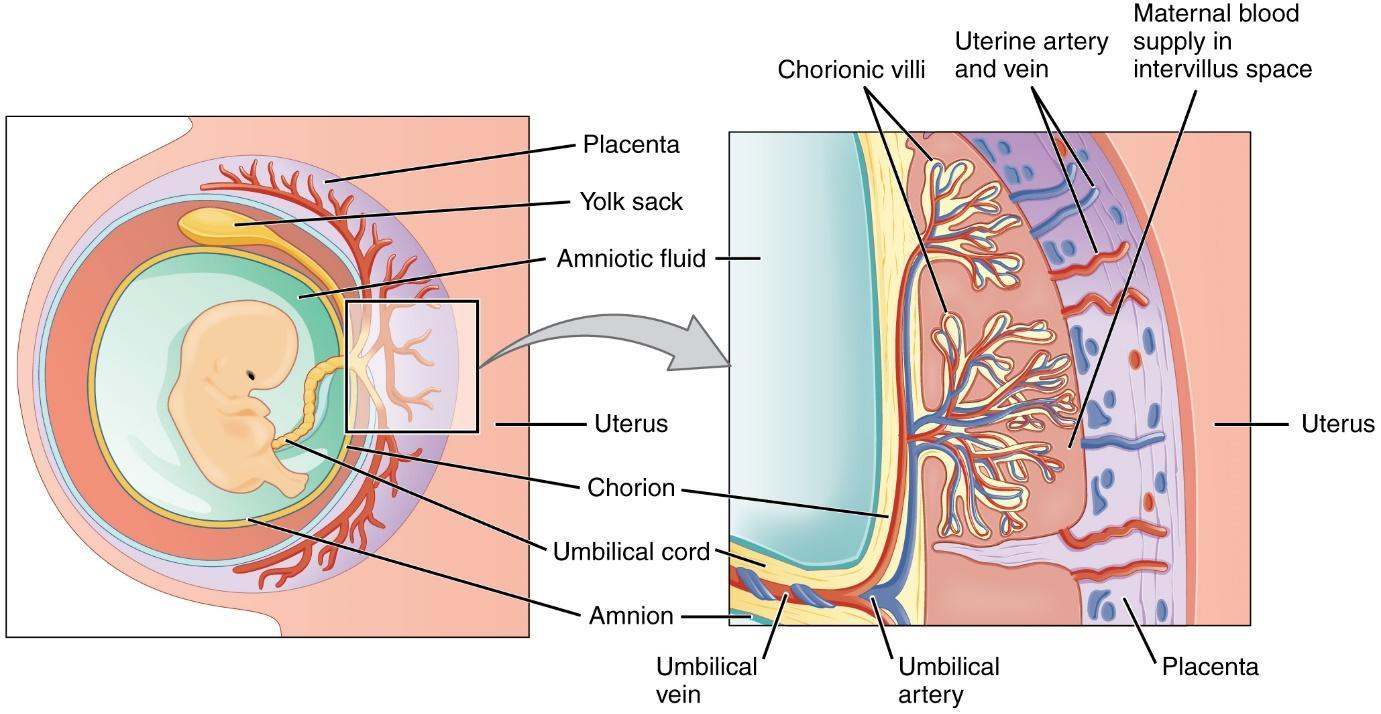
Structure of the placenta- The placenta is made up of both maternal tissue and embryonic tissue. The embryonic portion of the placenta is called the chorion. Chorion is made up of trophoblast, which is formed by multiplication of cells during implantation. The chorion forms a finger-like structure called chorion villa and is derived from the trophoblasts. These villi are surrounded by maternal blood and are a part of embryonic trophoblast cells. The space between the maternal blood and villi is called intervillous space.
Thus, the major two functions of the placenta are to
-Help the flow of gases from the foetus to the mother and in turn, helps in getting the nutrients.
-It also helps in removing the waste from the foetus and sending it to the mother’s blood.
Note: The placenta helps in the filtration of the microbes and preventing diseases like cold as infection. The foetal blood flows from the umbilical cord to the placenta. The tissues of the growing foetus do not incorporate embryonic trophoblasts but they are very important for the growth of the foetus.
Complete answer: The major function of the placenta is to provide nutrients to the foetus and develop the foetus. This is done in stages. First, the foetus gets attached to the uterine wall. It provides nutrients to the foetus and allows the foetus to transfer the waste material to the mother’s blood.
Structure of the placenta- The placenta is made up of both maternal tissue and embryonic tissue. The embryonic portion of the placenta is called the chorion. Chorion is made up of trophoblast, which is formed by multiplication of cells during implantation. The chorion forms a finger-like structure called chorion villa and is derived from the trophoblasts. These villi are surrounded by maternal blood and are a part of embryonic trophoblast cells. The space between the maternal blood and villi is called intervillous space.

Thus, the major two functions of the placenta are to
-Help the flow of gases from the foetus to the mother and in turn, helps in getting the nutrients.
-It also helps in removing the waste from the foetus and sending it to the mother’s blood.
Note: The placenta helps in the filtration of the microbes and preventing diseases like cold as infection. The foetal blood flows from the umbilical cord to the placenta. The tissues of the growing foetus do not incorporate embryonic trophoblasts but they are very important for the growth of the foetus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




