
Explain the sulphonation of benzene with reaction.
Answer
581.7k+ views
Hint: Benzene is highly prone to electrophilic substitution reactions. It contains delocalized electrons spanning over carbon atoms in the ring and it is highly attractive to electrophiles and is also highly stable to electrophilic substitutions.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is one of the most important organic compounds with the chemical formula ${C_6}{H_5}$ .It was discovered in 1825 by the English physicist Michael Faraday and was made available in large quantities in 1842. It is a colorless liquid and is a closed ring of six carbon atoms linked by bonds that alternate between single and double bonds.
Now, sulphonation of benzene is a process of heating benzene with fuming sulphuric acid to produce benzene sulfonic acid. This reaction is generally reversible in nature. Further, due to higher electronegativity, the oxygen present in sulfuric acid pulls an electron towards itself and generates an electrophile. This attacks the benzene ring and thus leads to the formation of benzene sulphonic acid. The reaction is as shown:
The reaction is as shown:
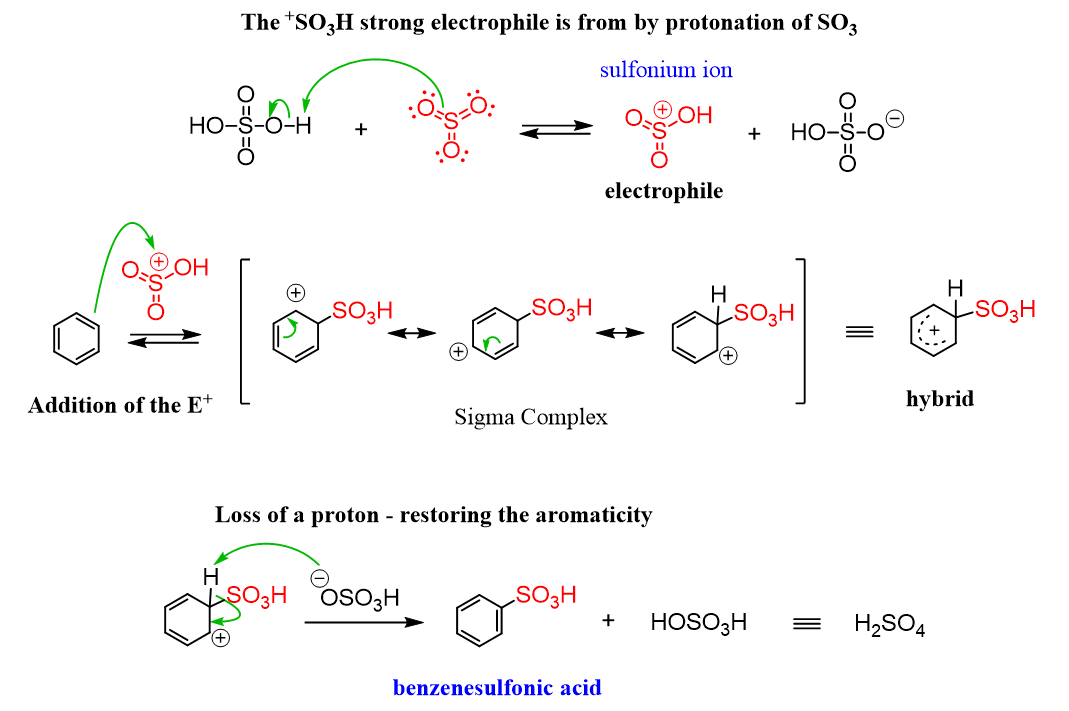
Moreover, benzene is an aromatic compound as the \[C - C\] bonds formed in the ring are not exactly single or double, rather they are of intermediate length. Further, according to the Huckel rule, for a ring to be aromatic, it should follow the property of planarity, complete delocalization of the pi electrons in the ring and presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring.
Note: The department of health and human services has recognized that benzene is a carcinogen i.e. it may cause cancer. Moreover, it is a widely used solvent which occurs in gasoline, car emissions and cigarette smoke. It is also used in the manufacturing of nylon fibers and in preparation of phenol.
Complete step by step answer:
Benzene is one of the most important organic compounds with the chemical formula ${C_6}{H_5}$ .It was discovered in 1825 by the English physicist Michael Faraday and was made available in large quantities in 1842. It is a colorless liquid and is a closed ring of six carbon atoms linked by bonds that alternate between single and double bonds.
Now, sulphonation of benzene is a process of heating benzene with fuming sulphuric acid to produce benzene sulfonic acid. This reaction is generally reversible in nature. Further, due to higher electronegativity, the oxygen present in sulfuric acid pulls an electron towards itself and generates an electrophile. This attacks the benzene ring and thus leads to the formation of benzene sulphonic acid. The reaction is as shown:
The reaction is as shown:

Moreover, benzene is an aromatic compound as the \[C - C\] bonds formed in the ring are not exactly single or double, rather they are of intermediate length. Further, according to the Huckel rule, for a ring to be aromatic, it should follow the property of planarity, complete delocalization of the pi electrons in the ring and presence of $(4n + 2)\pi $ electrons in the ring.
Note: The department of health and human services has recognized that benzene is a carcinogen i.e. it may cause cancer. Moreover, it is a widely used solvent which occurs in gasoline, car emissions and cigarette smoke. It is also used in the manufacturing of nylon fibers and in preparation of phenol.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




