
Explain the term congruent angles with the help of suitable example diagrams.
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: To explain congruent angles we have to recall the basic definition of congruent angles first. So, basically congruent angles are two angles or more than two angles that have the same measurement.
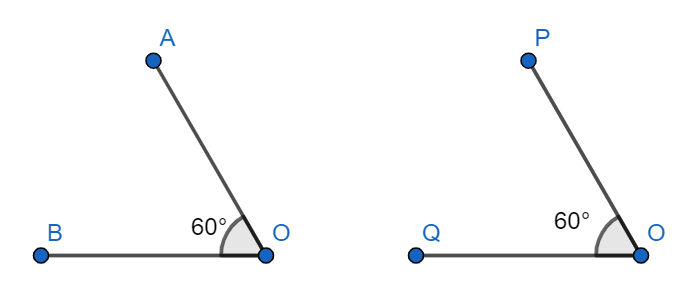
In the above example $\angle AOB\simeq \angle POQ$ both are ${{60}^{{}^\circ }}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
It is given in the question that we have to define congruent angle and list some examples of congruent angles. So, basically, congruent angles are the two or more than two angles that have the same measurements. If we say in more simple words then we can say that, when two angles have the same degree than they are said to be congruent angles.
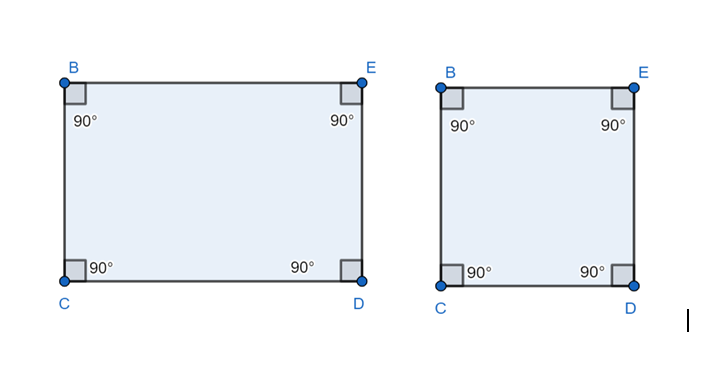
It is noted that it is not necessary to point the angle in the same direction, they don’t have to be on similar sized lines, but just the same angle measurements. Like- all the angles of the rectangle or square are congruent angles.
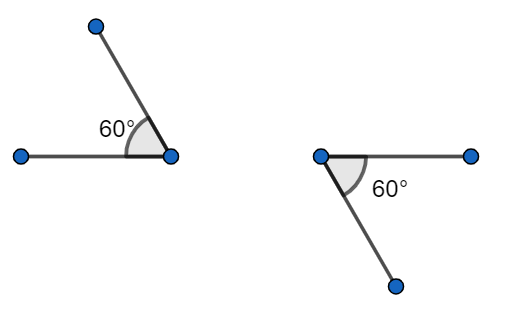
Angle (b) Angle
Angle (a) and angle (b) are congruent angles or we can say that angle a is congruent to angle b as both of them measure ${{60}^{{}^\circ }}$each.
Note: This is a very basic question of mathematics but generally students are confused because of incomplete information about the congruency of the angles. Students think that two angles are congruent if they have the same measurement as well as they are projected in the same direction which is not true. If two angles have the same measurement irrespective of the projection, they are said to be congruent angles.
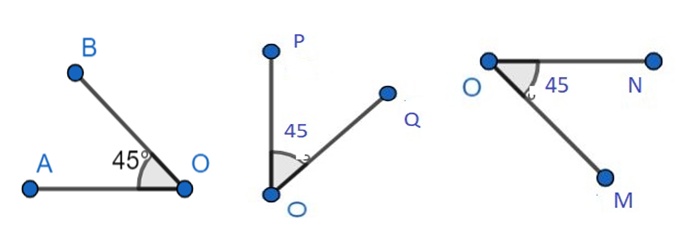
For example, in the given figure, all the angles are congruent to each other. That is, if all the angles $\angle AOB=\angle POQ=\angle NOM={{45}^{{}^\circ }}$, then they are congruent, irrespective of their projection.

In the above example $\angle AOB\simeq \angle POQ$ both are ${{60}^{{}^\circ }}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
It is given in the question that we have to define congruent angle and list some examples of congruent angles. So, basically, congruent angles are the two or more than two angles that have the same measurements. If we say in more simple words then we can say that, when two angles have the same degree than they are said to be congruent angles.
It is noted that it is not necessary to point the angle in the same direction, they don’t have to be on similar sized lines, but just the same angle measurements. Like- all the angles of the rectangle or square are congruent angles.


Angle (b) Angle
Angle (a) and angle (b) are congruent angles or we can say that angle a is congruent to angle b as both of them measure ${{60}^{{}^\circ }}$each.
Note: This is a very basic question of mathematics but generally students are confused because of incomplete information about the congruency of the angles. Students think that two angles are congruent if they have the same measurement as well as they are projected in the same direction which is not true. If two angles have the same measurement irrespective of the projection, they are said to be congruent angles.

For example, in the given figure, all the angles are congruent to each other. That is, if all the angles $\angle AOB=\angle POQ=\angle NOM={{45}^{{}^\circ }}$, then they are congruent, irrespective of their projection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 7 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

Convert 200 Million dollars in rupees class 7 maths CBSE

List of coprime numbers from 1 to 100 class 7 maths CBSE

AIM To prepare stained temporary mount of onion peel class 7 biology CBSE

The plural of Chief is Chieves A True B False class 7 english CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of the national daily class 7 english CBSE





