
Explain the terms primary and secondary structures of proteins. What is the difference between $ \alpha - $ helix and $ \beta - $ pleated sheet structure of proteins?
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: The three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule is known as protein structure. Proteins are polymers – especially polypeptides – made up of amino acid sequences, which are the polymer's monomers. A single amino acid monomer is also known as a residue, which denotes a polymer's repeating unit.
Complete answer:
Primary Structure: Every protein has one or more polypeptide chains as its primary structure. A-amino acids are connected in a precise order to form these chains. Primary structure refers to the specificity of sequence attachment.
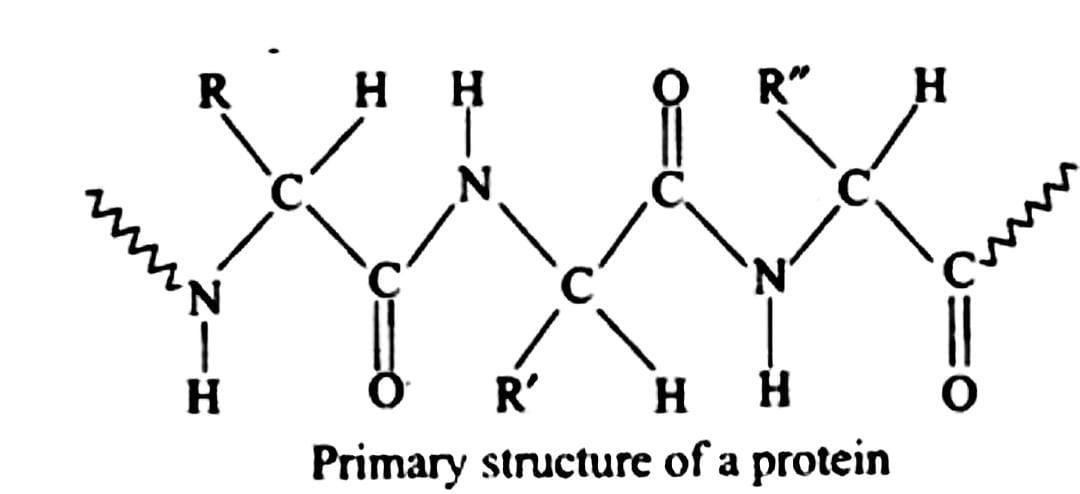
The main structure of proteins is determined by repeated hydrolysis in the presence of mineral acids. In each step of the process, the molecular mass of the products decreases, as shown below:
Proteins → Proteoses → Peptones → Polypeptides →Simple Peptides → $ \alpha - $ Amino acids
Secondary structure: Secondary structure is the consequence of the folding and organisation of polypeptide chains. It also gives the protein molecule a certain shape. This folding produces two different types of structures:
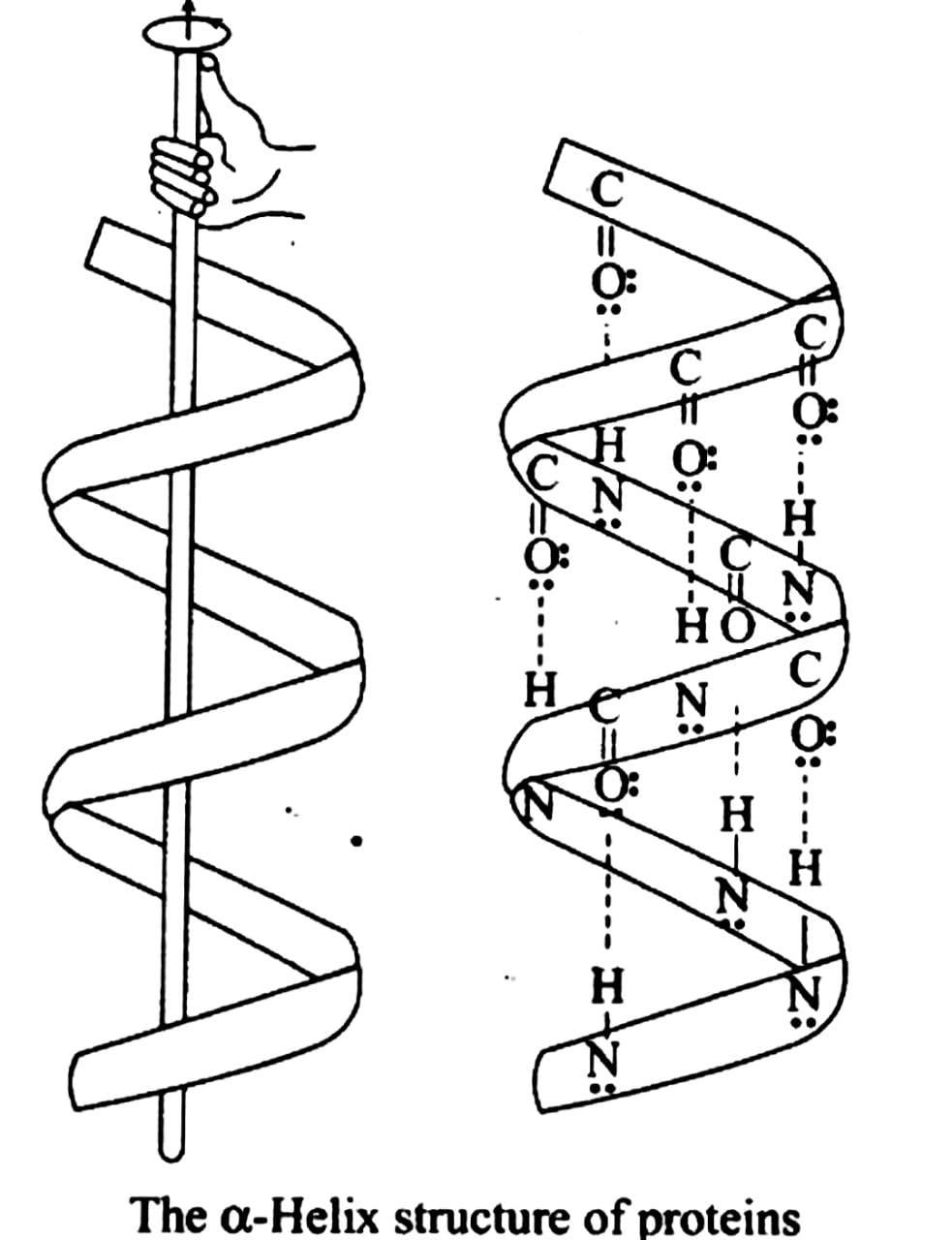
$ \alpha - $ Helix structure: The h-bonds are twisted in a right-handed fashion, with extra $ - NH $ groups connected with $ - C{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}O $ groups at neighbouring turns in this structure, which is a highly frequent folding pattern of polypeptide chains. As a result, the structure is known as the $ 3.613 $ helix. $ 3.16 $ amino acids make up the pitch of the helix. Between one amide group and a carbonyl group, hydrogen bonding forms the backbone of this structure.
$ \beta - $ pleated sheet structure: The zigzag arrangement of polypeptide chains next to one another and fixed at a common distance. Chains are held together by intermolecular H-bonds, and several chains unite to form a sheet. $ \beta - $ Pleated sheet structure is the name given to a 3-D arrangement of these sheets stacked on top of one other, which resembles draperies.

Note:
Polypeptides escape the ribosome largely as a random coil and fold into their native state as they are translated. The amino acid sequence of a protein chain is thought to determine the chain's final structure.
Complete answer:
Primary Structure: Every protein has one or more polypeptide chains as its primary structure. A-amino acids are connected in a precise order to form these chains. Primary structure refers to the specificity of sequence attachment.

The main structure of proteins is determined by repeated hydrolysis in the presence of mineral acids. In each step of the process, the molecular mass of the products decreases, as shown below:
Proteins → Proteoses → Peptones → Polypeptides →Simple Peptides → $ \alpha - $ Amino acids
Secondary structure: Secondary structure is the consequence of the folding and organisation of polypeptide chains. It also gives the protein molecule a certain shape. This folding produces two different types of structures:
$ \alpha - $ Helix structure: The h-bonds are twisted in a right-handed fashion, with extra $ - NH $ groups connected with $ - C{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}O $ groups at neighbouring turns in this structure, which is a highly frequent folding pattern of polypeptide chains. As a result, the structure is known as the $ 3.613 $ helix. $ 3.16 $ amino acids make up the pitch of the helix. Between one amide group and a carbonyl group, hydrogen bonding forms the backbone of this structure.

$ \beta - $ pleated sheet structure: The zigzag arrangement of polypeptide chains next to one another and fixed at a common distance. Chains are held together by intermolecular H-bonds, and several chains unite to form a sheet. $ \beta - $ Pleated sheet structure is the name given to a 3-D arrangement of these sheets stacked on top of one other, which resembles draperies.

Note:
Polypeptides escape the ribosome largely as a random coil and fold into their native state as they are translated. The amino acid sequence of a protein chain is thought to determine the chain's final structure.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




