
Explain the terms tenuinucellate and crassinucellate.
Answer
501k+ views
Hint: The ovule's body is made up of a mass of parenchymatous cells known as the nucellus. Nucellus takes advantage of the ovule. It protects the embryo sac. Because they have an abundance of food reserves, they serve as nutritive tissues for the embryo in some plants.
Complete answer:
The ovary contains one or more ovules or megasporangium, which are circular or oval structures. It is connected to the placenta by a stalk known as the funiculus. The nucellus is the central, bulky part of the ovule. The nucellus is the tissue that makes up the majority of the ovule in seed plants. It houses the embryo sac as well as the nutritive tissue.
Except for a small gap called the micropyle, it is completely surrounded by the integuments. It may persist after fertilisation in certain flowering plants and provide nutrients to the embryo.The ovules are classified into the following types based on the development of the nucellus:
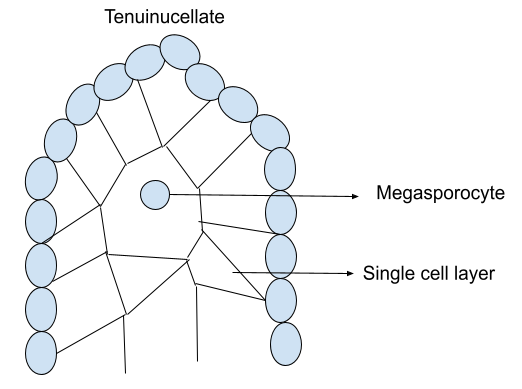
(1) Tenuinucellate- The archesporium or archesporial cell does not divide and serves as the megaspore mother cell directly. Because of the single layered nucellar epidermis, the sporogenous cell or megaspore mother cell is hypodermal.The sporogenous cell is termed tenuinucellate if it is hypodermal with a single layer of nucellar tissue surrounding it. The nucellus of tenuinucellate ovules is typically very small.
(2) Crassinucellate- The archesporium divides into outer parietal cells and inner sporogenous cells, the latter of which serves as the mother cell of megaspores. Because of the formation of parietal cells, which remain undivided or divide to form parietal tissue, the sporogenous cell is sub-hypodermal.
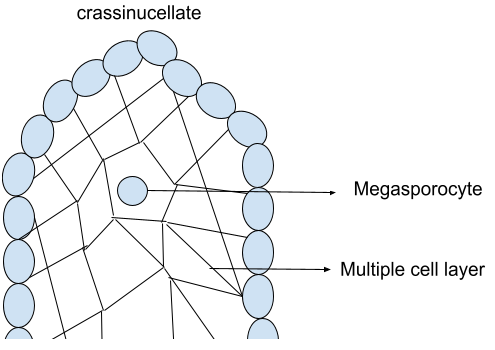
The presence of two or more cell layers between the megasporocyte and the epidermal cells during the megasporophyte's early development. The megasporocyte develops into the embryo sac, which contains the egg, which will develop into the embryo if fertilised and the conditions are favourable.
Note: The nucellus may develop into the perisperm that feeds the embryo after fertilisation. In some plants, the diploid tissue of the nucellus can give rise to the embryo within the seed via an asexual reproduction mechanism known as nucellar embryony.
Complete answer:
The ovary contains one or more ovules or megasporangium, which are circular or oval structures. It is connected to the placenta by a stalk known as the funiculus. The nucellus is the central, bulky part of the ovule. The nucellus is the tissue that makes up the majority of the ovule in seed plants. It houses the embryo sac as well as the nutritive tissue.
Except for a small gap called the micropyle, it is completely surrounded by the integuments. It may persist after fertilisation in certain flowering plants and provide nutrients to the embryo.The ovules are classified into the following types based on the development of the nucellus:
(1) Tenuinucellate- The archesporium or archesporial cell does not divide and serves as the megaspore mother cell directly. Because of the single layered nucellar epidermis, the sporogenous cell or megaspore mother cell is hypodermal.The sporogenous cell is termed tenuinucellate if it is hypodermal with a single layer of nucellar tissue surrounding it. The nucellus of tenuinucellate ovules is typically very small.

(2) Crassinucellate- The archesporium divides into outer parietal cells and inner sporogenous cells, the latter of which serves as the mother cell of megaspores. Because of the formation of parietal cells, which remain undivided or divide to form parietal tissue, the sporogenous cell is sub-hypodermal.

The presence of two or more cell layers between the megasporocyte and the epidermal cells during the megasporophyte's early development. The megasporocyte develops into the embryo sac, which contains the egg, which will develop into the embryo if fertilised and the conditions are favourable.
Note: The nucellus may develop into the perisperm that feeds the embryo after fertilisation. In some plants, the diploid tissue of the nucellus can give rise to the embryo within the seed via an asexual reproduction mechanism known as nucellar embryony.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




