
Explain the working of a half-wave diode rectifier.
Answer
591.6k+ views
Hint: A device that converts alternating current or a.c. into direct current, d.c. is known as a rectifier. It is called a half-wave rectifier because it allows only one-half cycle of alternating current to pass through it. When a single p-n junction diode is connected with a load resistor in series combination, it forms a simple half-wave rectifier.
Complete step by step solution:
Step I:
A Half Wave Rectifier consists of a single p-n junction diode connected in series to the load resistor. A diode is to electric current like a one-way valve, it allows electric current to flow in only one direction. This property of the diode is used in creating simple rectifiers. AC voltage is applied to the primary side of the transformer and at the winding a low voltage source is attached to the diode. The secondary coil is connected to the junction diode by a load resistance.
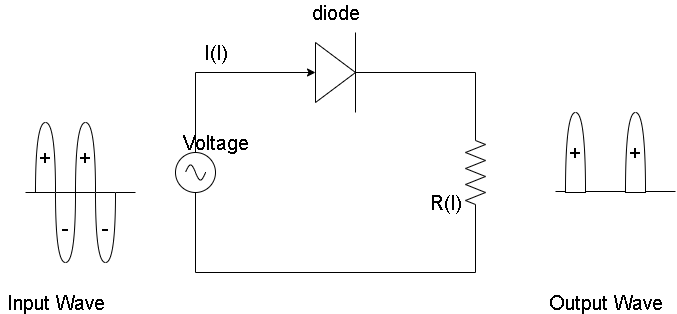
Step II:
During the positive half cycle, the current is made to pass through the primary coil and an induced e.m.f. is set up in the secondary coil due to mutual induction. The circuit is forward bias during the positive half cycle. This is because the direction of induced e.m.f. is such that it makes the upper end of the secondary coil positive and lower end negative. The output current flows in the circuit along with some voltage drop.
Step III:
During the negative half-cycle, the process is completely reversed. This means the upper end of the secondary coil is negative and the lower end is positive, thus making the circuit reverse biased. Since it is now an open circuit, so no current passes and no output voltage is obtained.
Note:
When an alternating current is passed through a half-wave rectifier, only half cycle continues. The other half cycle is blocked on the D.C. side. The ratio of d.c power output to a.c. power input is called rectifier efficiency which is approximately 40.6%.
Complete step by step solution:
Step I:
A Half Wave Rectifier consists of a single p-n junction diode connected in series to the load resistor. A diode is to electric current like a one-way valve, it allows electric current to flow in only one direction. This property of the diode is used in creating simple rectifiers. AC voltage is applied to the primary side of the transformer and at the winding a low voltage source is attached to the diode. The secondary coil is connected to the junction diode by a load resistance.

Step II:
During the positive half cycle, the current is made to pass through the primary coil and an induced e.m.f. is set up in the secondary coil due to mutual induction. The circuit is forward bias during the positive half cycle. This is because the direction of induced e.m.f. is such that it makes the upper end of the secondary coil positive and lower end negative. The output current flows in the circuit along with some voltage drop.
Step III:
During the negative half-cycle, the process is completely reversed. This means the upper end of the secondary coil is negative and the lower end is positive, thus making the circuit reverse biased. Since it is now an open circuit, so no current passes and no output voltage is obtained.
Note:
When an alternating current is passed through a half-wave rectifier, only half cycle continues. The other half cycle is blocked on the D.C. side. The ratio of d.c power output to a.c. power input is called rectifier efficiency which is approximately 40.6%.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




