
Explain, using a labeled diagram, the principle and working of a moving coil galvanometer. What is the function of (i) uniform radial magnetic field, (ii) soft iron core?
Define the terms (i) current sensitivity and (ii) voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. Why does increasing the current sensitivity not necessarily increase voltage sensitivity?
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint :Galvanometer is an instrument which is used to measure electric currents. It works on lower values of current as compared to an ammeter. A moving coil galvanometer works on the concept of change in magnetic flux as given by Faraday's law. It converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
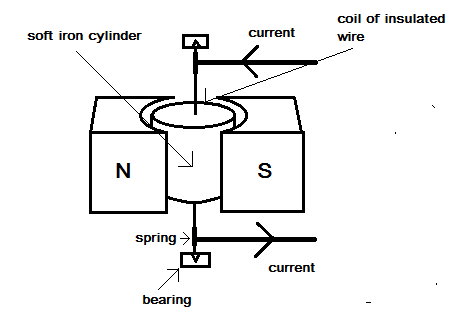
A galvanometer is an electromechanical instrument used for the detection of electric currents flowing through electrical circuits. It is a very sensitive instrument which cannot be used for the measurement of large currents. It works on the principle of conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy while a current is flowing in a magnetic field as it experiences a magnetic torque and hence rotates through an angle proportional to the current flowing through it.
By making a uniform radial magnetic field through a coil, the magnetic field lines become perpendicular to the magnetic moment of a galvanometer.
Soft Iron core can make the electromechanical field radial which in turn would increase the magnetic field.
Current Sensitivity- It is deflection produced per unit current flowing across the galvanometer.
Voltage Sensitivity- It is the minimum change in voltage which produces change in the output of the galvanometer.
Since Voltage sensitivity decreases with the increase in resistance of the coil and the effect of an increase in the number of turns is hence nullified in case of voltage sensitivity so there is no change of voltage sensitivity, whenever there is a change in current sensitivity.
Note :
The moving coil galvanometer works on the principle of change in flux and as there is relative motion between the coil and the magnets, the flux across the coil changes which produces current and hence electromagnetic induction takes place. There has to be non zero relative motion between the coil and the magnets.
Complete Step By Step Answer:

A galvanometer is an electromechanical instrument used for the detection of electric currents flowing through electrical circuits. It is a very sensitive instrument which cannot be used for the measurement of large currents. It works on the principle of conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy while a current is flowing in a magnetic field as it experiences a magnetic torque and hence rotates through an angle proportional to the current flowing through it.
By making a uniform radial magnetic field through a coil, the magnetic field lines become perpendicular to the magnetic moment of a galvanometer.
Soft Iron core can make the electromechanical field radial which in turn would increase the magnetic field.
Current Sensitivity- It is deflection produced per unit current flowing across the galvanometer.
Voltage Sensitivity- It is the minimum change in voltage which produces change in the output of the galvanometer.
Since Voltage sensitivity decreases with the increase in resistance of the coil and the effect of an increase in the number of turns is hence nullified in case of voltage sensitivity so there is no change of voltage sensitivity, whenever there is a change in current sensitivity.
Note :
The moving coil galvanometer works on the principle of change in flux and as there is relative motion between the coil and the magnets, the flux across the coil changes which produces current and hence electromagnetic induction takes place. There has to be non zero relative motion between the coil and the magnets.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




