
Explain why phenolphthalein is used as an indicator in acid-base titration.
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: Phenolphthalein remains colourless in acidic medium. However, when the solution becomes basic i.e. pH > 7, the solution becomes pink due to phenolphthalein. Understand the change in the structure of phenolphthalein when a base is added to it.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that indicators are those substances which are often used in titrations as a visual indication of when the equivalence point is reached. Knowing the equivalence point allows for the determination of the unknown concentration of analyte using the addition of the known concentration.
We know what acid-base titration is. In an acid-base titration, the neutralization of an acid takes place by a base. In acid-base titration, we take a known amount of acid in conical flask and add some phenolphthalein indicator. To know what is happening here, we need to analyse the structure of phenolphthalein in both acidic and basic mediums.
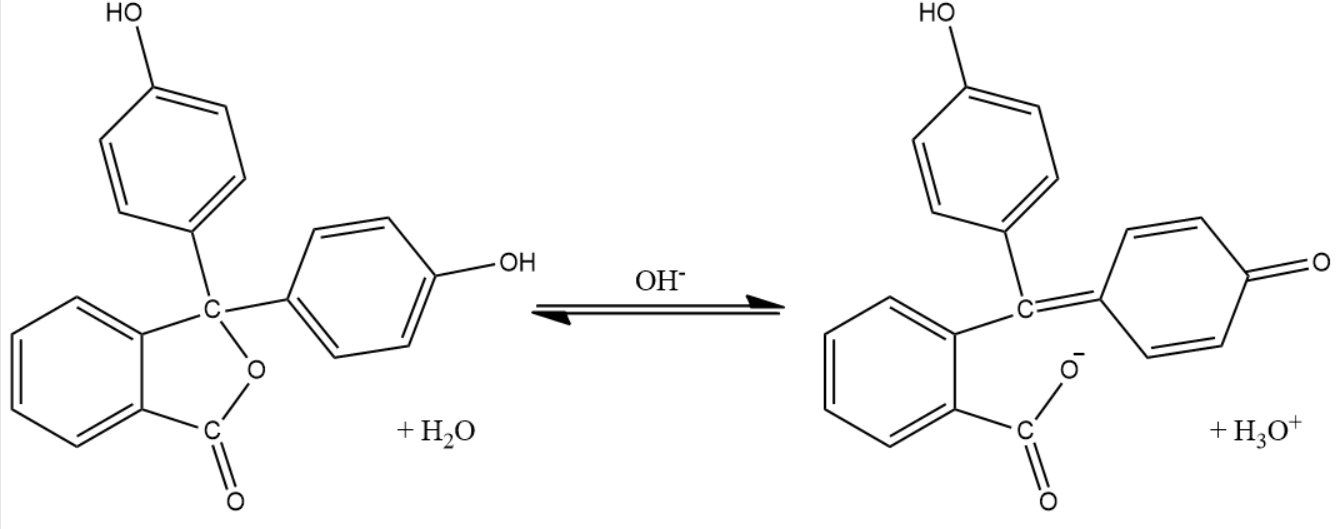
Initially, pH of the solution in the conical flask is less than 7 since it is acidic. So, the solution becomes colourless because the phenolphthalein is colourless in an acidic medium. After the equivalence point is reached, the very next drop makes the solution basic. In basic solution, the acidic proton in the phenolphthalein will be captured by the hydroxide ions and forms a quinoid structure which is pink in colour. So, this appearance of pink colour will help to identify the end point of this titration.
Due to this structural importance, phenolphthalein is used as an indicator in acid-base titration.
Note: You need to notice that many different substances can be used as indicators, depending on the particular reaction to be monitored. In all cases, a good indicator must have some properties. They are, the colour change must be easily detected, and the colour change must be rapid. Also, the indicator molecule must not react with the substance being titrated.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that indicators are those substances which are often used in titrations as a visual indication of when the equivalence point is reached. Knowing the equivalence point allows for the determination of the unknown concentration of analyte using the addition of the known concentration.
We know what acid-base titration is. In an acid-base titration, the neutralization of an acid takes place by a base. In acid-base titration, we take a known amount of acid in conical flask and add some phenolphthalein indicator. To know what is happening here, we need to analyse the structure of phenolphthalein in both acidic and basic mediums.

Initially, pH of the solution in the conical flask is less than 7 since it is acidic. So, the solution becomes colourless because the phenolphthalein is colourless in an acidic medium. After the equivalence point is reached, the very next drop makes the solution basic. In basic solution, the acidic proton in the phenolphthalein will be captured by the hydroxide ions and forms a quinoid structure which is pink in colour. So, this appearance of pink colour will help to identify the end point of this titration.
Due to this structural importance, phenolphthalein is used as an indicator in acid-base titration.
Note: You need to notice that many different substances can be used as indicators, depending on the particular reaction to be monitored. In all cases, a good indicator must have some properties. They are, the colour change must be easily detected, and the colour change must be rapid. Also, the indicator molecule must not react with the substance being titrated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




