
Explain with a circuit diagram how to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter.
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: As we all know ammeter is an instrument with low resistance. In order to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a low shunt resistance should be connected in parallel to resistance of the galvanometer ${{R}_{G}}$. So that the overall resistance of the circuit becomes smaller.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us check the circuit diagram.
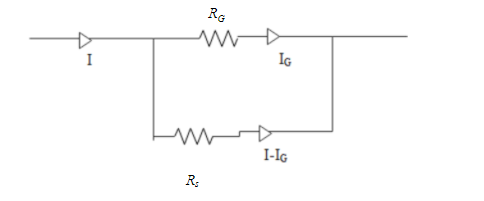
Here
${{R}_{G}}$ Is the resistance of the galvanometer and ${{R}_{s}}$ is the shunt resistance (a very low resistance) we add to the circuit.
$I$ is the total current flowing into the circuit and ${{l}_{G}}$ is the current flowing through the galvanometer.
$I-{{l}_{G}}$ is the current flowing through shunt resistance. As we all know ammeter is an instrument with low resistance. In order to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a low shunt resistance should be connected in parallel to resistance of the galvanometer${{R}_{G}}$. So that the overall resistance of the circuit becomes smaller. Thus a galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by adding a low shunt resistance in parallel to the galvanometer.
Additional information:
Ammeter is an instrument used for measuring either alternating electric current or direct current. It is measured in amperes. An ammeter can measure a wide range of current values. It is because only a small portion of the current is directed through the meter at high voltages. The shunt resistance parallel to the galvanometer is taking up the major portion of current. This is the making of an ammeter.
Note: In order to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a shunt resistance is needed to be connected parallel to the galvanometer. In order to convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter, a very high resistance called series resistance is to be connected in series.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us check the circuit diagram.

Here
${{R}_{G}}$ Is the resistance of the galvanometer and ${{R}_{s}}$ is the shunt resistance (a very low resistance) we add to the circuit.
$I$ is the total current flowing into the circuit and ${{l}_{G}}$ is the current flowing through the galvanometer.
$I-{{l}_{G}}$ is the current flowing through shunt resistance. As we all know ammeter is an instrument with low resistance. In order to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a low shunt resistance should be connected in parallel to resistance of the galvanometer${{R}_{G}}$. So that the overall resistance of the circuit becomes smaller. Thus a galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by adding a low shunt resistance in parallel to the galvanometer.
Additional information:
Ammeter is an instrument used for measuring either alternating electric current or direct current. It is measured in amperes. An ammeter can measure a wide range of current values. It is because only a small portion of the current is directed through the meter at high voltages. The shunt resistance parallel to the galvanometer is taking up the major portion of current. This is the making of an ammeter.
Note: In order to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter, a shunt resistance is needed to be connected parallel to the galvanometer. In order to convert a galvanometer into a voltmeter, a very high resistance called series resistance is to be connected in series.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




