
Extrachromosomal DNA used as a vector in gene cloning is
(a)Transposon
(b)Intron
(c)Exon
(d)Plasmid
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint Gene cloning is the process of copying fragments of DNA that can be used for different purposes such as the creation of genetically modified crops or for curing a disease.
Complete answer:
The plasmid is an extrachromosomal DNA which is used as a vector in gene cloning. It is physically separated from the chromosomal DNA and replicates separately and is a small molecule in a cell. They are found as small circular and double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and are present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. They carry genes that benefit the survival of the organisms and advantage as antibiotic resistance. They are small and contain only additional genes that are useful in certain situations and conditions whereas the chromosomes are large and contain essential genetic information for normal conditions. Some artificial plasmids are used as vectors in molecular cloning which serve as the replication of recombinant DNA sequences in the host organisms. They are introduced in the laboratory with cell transformation. They possess a stretch of DNA that acts as an origin of replication for the replication of plasmid independently. A replicon is a self-replicating unit that consists of several.
Additional information:
Transposon: It is a DNA sequence that changes its position and creates or reverse mutation. It alters the cell's genetic identity and genome size which results in the duplication of the same genetic material. They constitute a large fraction of the genome which is responsible for the mass of DNA in a eukaryotic cell. They are important in genome functioning and evolution and are selfish genetic elements.
Intron: It is a nucleotide sequence in a gene that is removed by the RNA splicing during the process of maturation of the final RNA product. The sequences are joined together in the final mature RNA after the splicing which is exons. They are found in the genes of many organisms and viruses that are located in various genes which include the generation of proteins and ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA.
Exon: It is a part of a gene that encodes the final mature RNA that is produced by the gene after introns and is removed by RNA splicing. The exons are covalently joined to each other in RNA splicing which is a part of generating the mature messenger RNA. They include the protein-coding sequence and untranslated regions in the protein-coding genes.
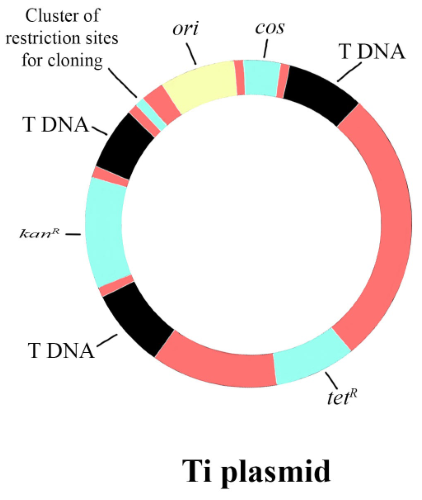
So, the correct answer is 'Plasmid'.
Note: The transposon varies in different forms and shapes and can change their position within a genome. They are not randomly distributed in the genome and are an extensive source of genetic polymorphism and mutation. They are the insertional mutagens in both germline and Soma.
Complete answer:
The plasmid is an extrachromosomal DNA which is used as a vector in gene cloning. It is physically separated from the chromosomal DNA and replicates separately and is a small molecule in a cell. They are found as small circular and double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria and are present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. They carry genes that benefit the survival of the organisms and advantage as antibiotic resistance. They are small and contain only additional genes that are useful in certain situations and conditions whereas the chromosomes are large and contain essential genetic information for normal conditions. Some artificial plasmids are used as vectors in molecular cloning which serve as the replication of recombinant DNA sequences in the host organisms. They are introduced in the laboratory with cell transformation. They possess a stretch of DNA that acts as an origin of replication for the replication of plasmid independently. A replicon is a self-replicating unit that consists of several.
Additional information:
Transposon: It is a DNA sequence that changes its position and creates or reverse mutation. It alters the cell's genetic identity and genome size which results in the duplication of the same genetic material. They constitute a large fraction of the genome which is responsible for the mass of DNA in a eukaryotic cell. They are important in genome functioning and evolution and are selfish genetic elements.
Intron: It is a nucleotide sequence in a gene that is removed by the RNA splicing during the process of maturation of the final RNA product. The sequences are joined together in the final mature RNA after the splicing which is exons. They are found in the genes of many organisms and viruses that are located in various genes which include the generation of proteins and ribosomal RNA and transfer RNA.
Exon: It is a part of a gene that encodes the final mature RNA that is produced by the gene after introns and is removed by RNA splicing. The exons are covalently joined to each other in RNA splicing which is a part of generating the mature messenger RNA. They include the protein-coding sequence and untranslated regions in the protein-coding genes.

So, the correct answer is 'Plasmid'.
Note: The transposon varies in different forms and shapes and can change their position within a genome. They are not randomly distributed in the genome and are an extensive source of genetic polymorphism and mutation. They are the insertional mutagens in both germline and Soma.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




