
${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation is produced as a result of
(a)crossing${ F }_{ 1 }$ individual with dominant individuals
(b)crossing ${ F }_{ 1 }$ individuals with recessive individuals
(c)crossing ${ F }_{ 1 }$ individual amongst themselves
(d)all the above
Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint: The crossing of heterozygotes that are phenotypically and genotypically similar to the parent organisms results in the formation of the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generations.
Complete answer:
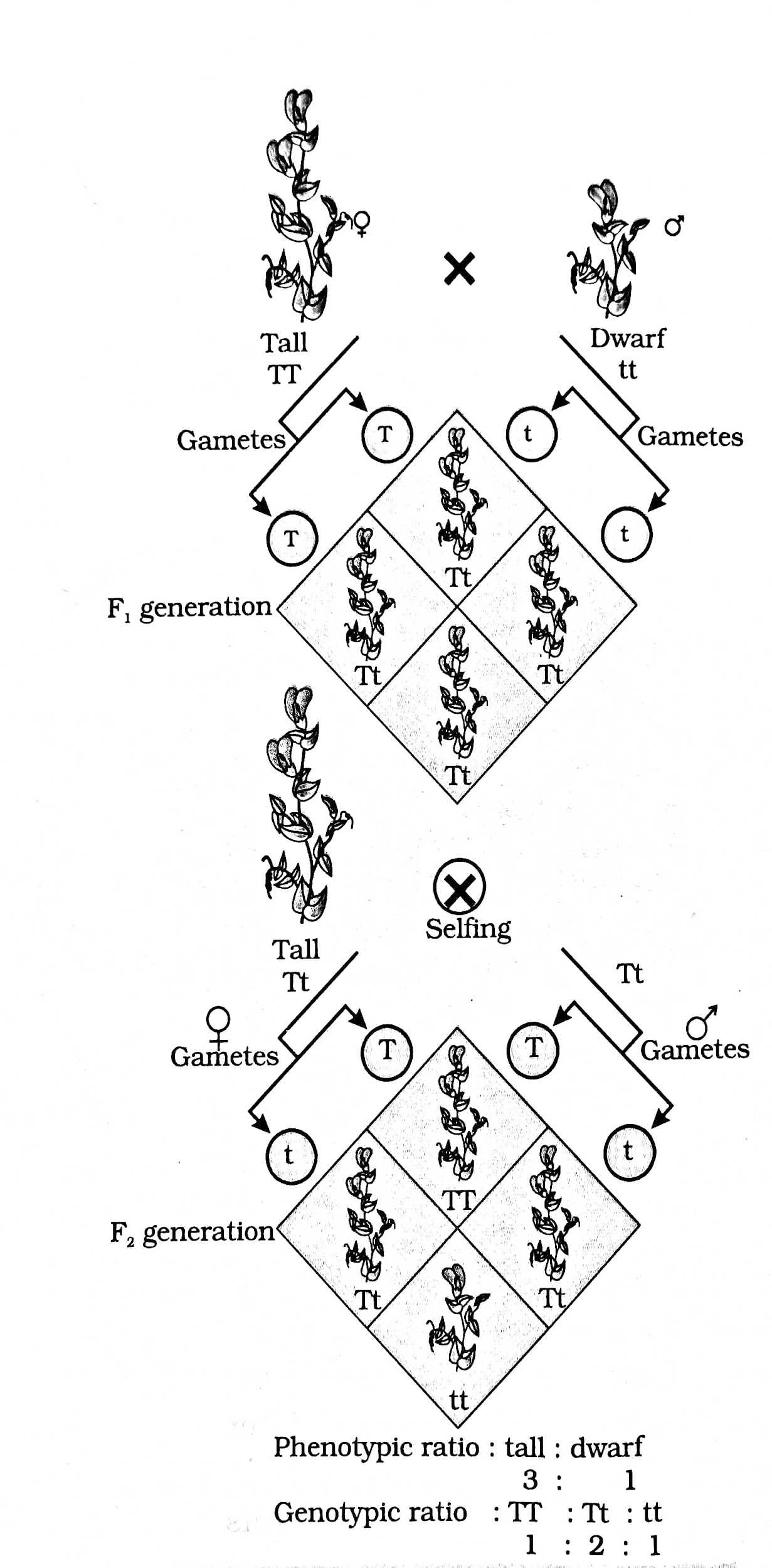
${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation or second filial generation is formed when the gametes are crossed with the same individuals formed from the first hybrid plants i.e, in the first generation or first filial generation. This was observed by the G.Mendel while doing experiments on tall and dwarf pea plants.
Additional Information: - Gregor John Mendel discovered the basic principles of hereditary.
- When two genes of different characters are crossed and the obtained individual is considered as first filial generation or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation
- When the gametes of the parent species are crossed with the dominant or recessive genotype of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation or crossing between themselves resulting in the formation of the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generations. G.Mendel first observed the second filial generation when pea plants of first-generation crossed among themselves.
-The descriptive terms of a species is called a genotype and the genes are called a phenotype.
- Phenotype can be known by observing the resulting species bur genotype cannot be seen. To determine the genotype of the plant at ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation plant should be crossed with recessive genotypes. This is called 'test cross'.
- If the heterozygotes of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation is crossed with a similar genotype or phenotype of parent it is called 'back cross'.
So, the correct answer is ''${ F }_{ 1 }$ individuals amongst themselves”.
Note: A test cross is a kind of back cross.
The crossing of the dominant phenotype with the recessive phenotype is called the monohybrid cross.
To understand the inheritance in monohybrid cross G.Mendel proposed two rules called "principles of inheritance" namely 'Law of dominance and 'Law of segregation'.
Complete answer:
${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation or second filial generation is formed when the gametes are crossed with the same individuals formed from the first hybrid plants i.e, in the first generation or first filial generation. This was observed by the G.Mendel while doing experiments on tall and dwarf pea plants.
Additional Information: - Gregor John Mendel discovered the basic principles of hereditary.
- When two genes of different characters are crossed and the obtained individual is considered as first filial generation or ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation
- When the gametes of the parent species are crossed with the dominant or recessive genotype of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation or crossing between themselves resulting in the formation of the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generations. G.Mendel first observed the second filial generation when pea plants of first-generation crossed among themselves.
-The descriptive terms of a species is called a genotype and the genes are called a phenotype.
- Phenotype can be known by observing the resulting species bur genotype cannot be seen. To determine the genotype of the plant at ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation plant should be crossed with recessive genotypes. This is called 'test cross'.
- If the heterozygotes of ${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation is crossed with a similar genotype or phenotype of parent it is called 'back cross'.
So, the correct answer is ''${ F }_{ 1 }$ individuals amongst themselves”.
Note: A test cross is a kind of back cross.
The crossing of the dominant phenotype with the recessive phenotype is called the monohybrid cross.
To understand the inheritance in monohybrid cross G.Mendel proposed two rules called "principles of inheritance" namely 'Law of dominance and 'Law of segregation'.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




