
Fibrous protein collagen in its natural form has a
(A) Secondary structure
(B) Tertiary structure
(C) Quaternary structure
(D) Primary structure
Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint: Fibrous protein collagen in its natural form is a cluster of several protein chains or subunits. Each of the subunits of proteins has its own primary, secondary, and tertiary structure. It is an arrangement of multiple folded protein subunits in a multi- subunit complex.
Complete step by step answer:
Collagen is one of the major insoluble fibrous proteins present in the extracellular matrix and connective tissue. Fibrous protein collagen in its natural form has a Quaternary structure. Other examples of proteins with quaternary structure include hemoglobin, DNA polymerase, and ion channels.
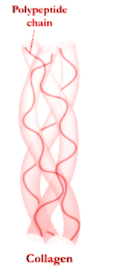
So, the correct answer is ‘Quaternary structure’.
Additional Information: Proteins are the polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer.
Protein structure is divided into four different types, they are as follows:
- Primary structure: The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids within a protein. For example Insulin.
- Secondary structure: The next level of protein structure, secondary structure, refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide because of interactions between atoms of the backbone. The most common sorts of secondary structures are the $\alpha$-helix and also the $\beta$-pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl O of 1 amino acid and also the amino H of another. For example Haemoglobin.
- Tertiary structure: Tertiary structure is defined as the three-dimensional structure of monomeric and multimeric protein molecules. The $\alpha$-helices and $\beta$-pleated sheets are folded into a more compact globular structure. For example keratin and immunoglobulin.
Quaternary structure: When some proteins are made up of multiple polypeptide chains, also known as subunits. When these subunits come together, they form the quaternary structure of the protein.
Note: Collagens are the major components of the bone (type I collagen), cartilage (type II collagen), blood vessels, tendons, and other body components. Like most fibrous proteins, collagen is also insoluble in an aqueous environment.
Complete step by step answer:
Collagen is one of the major insoluble fibrous proteins present in the extracellular matrix and connective tissue. Fibrous protein collagen in its natural form has a Quaternary structure. Other examples of proteins with quaternary structure include hemoglobin, DNA polymerase, and ion channels.

So, the correct answer is ‘Quaternary structure’.
Additional Information: Proteins are the polymers – specifically polypeptides – formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer.
Protein structure is divided into four different types, they are as follows:
- Primary structure: The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids within a protein. For example Insulin.
- Secondary structure: The next level of protein structure, secondary structure, refers to local folded structures that form within a polypeptide because of interactions between atoms of the backbone. The most common sorts of secondary structures are the $\alpha$-helix and also the $\beta$-pleated sheet. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds, which form between the carbonyl O of 1 amino acid and also the amino H of another. For example Haemoglobin.
- Tertiary structure: Tertiary structure is defined as the three-dimensional structure of monomeric and multimeric protein molecules. The $\alpha$-helices and $\beta$-pleated sheets are folded into a more compact globular structure. For example keratin and immunoglobulin.
Quaternary structure: When some proteins are made up of multiple polypeptide chains, also known as subunits. When these subunits come together, they form the quaternary structure of the protein.
Note: Collagens are the major components of the bone (type I collagen), cartilage (type II collagen), blood vessels, tendons, and other body components. Like most fibrous proteins, collagen is also insoluble in an aqueous environment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




