
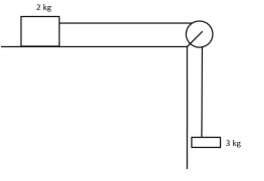
Find acceleration, normal reaction and tension in each case. $\left( {g = 10\,m/{s^2}} \right)$

Answer
579.6k+ views
Hint:This question is pretty simple if you know that tension on both parts of the strings is exactly the same around the pulley, since the strings are considered massless, the question gets even simpler. Also, the surfaces are given to be smooth, hence, there is no friction in the given question. All you need to do is to equate the tension and assume the acceleration of the $2{\kern 1pt} kg$ mass as $a$ which is the acceleration asked in the question.
Complete step by step answer:
We will proceed with the solution exactly as told in the hint section of the solution to the question.
Let us assume a tension ${T_1}$ in the vertical section of the string.
We’ve been given the mass of the lower block as ${M_1} = 3\,kg$
Using this, we can say that:
${T_1} = {M_1}g$
After substituting in the values, we get:
${T_1} = 30\,N$
Now, let’s assume a tension ${T_2}$ in the horizontal section of the string, since tension in the string around the pulley is always equal, we can say:
${T_2} = {T_1} = 30\,N$
Now, let us assume the mass ${M_2} = 2\,kg$ moving with an acceleration of magnitude $a$, now we can say that:
${M_2}a = {T_2}$
We’ve already found out the value of tension in the horizontal section of the string to be the same as the tension in the vertical section of the string. Using this, we can write:
$
\left( 2 \right)a = 30\,N \\
a = 15\,m/{s^2} \\
$
We also need to find the value of normal reaction force on the mass ${M_2}\,\left( { = \,2\,kg} \right)$
We know that normal force is the force perpendicular to the surface. Since there is no vertical movement of the mass ${M_2}$, we can safely say that the normal force in this case is equal to the weight of the box. Hence:
$
N = {M_2}g \\
N = 20\,N \\
$
We’ve found out the values of:
Acceleration, $a = 15\,m/{s^2}$
Normal reaction, $N = 20\,N$
Tension, $T = {T_1} = 30\,N$
Note: Many students commit mistakes by adding the two masses and finding the acceleration by dividing the tension with the combined mass. Although both of the boxes move with the same acceleration, you need to know that only the mass ${M_2}$ is contributing to the value of acceleration.
Complete step by step answer:
We will proceed with the solution exactly as told in the hint section of the solution to the question.
Let us assume a tension ${T_1}$ in the vertical section of the string.
We’ve been given the mass of the lower block as ${M_1} = 3\,kg$
Using this, we can say that:
${T_1} = {M_1}g$
After substituting in the values, we get:
${T_1} = 30\,N$
Now, let’s assume a tension ${T_2}$ in the horizontal section of the string, since tension in the string around the pulley is always equal, we can say:
${T_2} = {T_1} = 30\,N$
Now, let us assume the mass ${M_2} = 2\,kg$ moving with an acceleration of magnitude $a$, now we can say that:
${M_2}a = {T_2}$
We’ve already found out the value of tension in the horizontal section of the string to be the same as the tension in the vertical section of the string. Using this, we can write:
$
\left( 2 \right)a = 30\,N \\
a = 15\,m/{s^2} \\
$
We also need to find the value of normal reaction force on the mass ${M_2}\,\left( { = \,2\,kg} \right)$
We know that normal force is the force perpendicular to the surface. Since there is no vertical movement of the mass ${M_2}$, we can safely say that the normal force in this case is equal to the weight of the box. Hence:
$
N = {M_2}g \\
N = 20\,N \\
$
We’ve found out the values of:
Acceleration, $a = 15\,m/{s^2}$
Normal reaction, $N = 20\,N$
Tension, $T = {T_1} = 30\,N$
Note: Many students commit mistakes by adding the two masses and finding the acceleration by dividing the tension with the combined mass. Although both of the boxes move with the same acceleration, you need to know that only the mass ${M_2}$ is contributing to the value of acceleration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




