
Find the equation of the circle if the circle passes through the points (0, 0), (8, 0) and (0, 9).
Answer
612.6k+ views
Hint: First we will find the center and radius of the circle using distance formula and then we will find the equation of the circle from obtained data
Distance Formula, \[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Given that we have to find the equation of a circle passing through points (0, 0), (8, 0) and (0, 9) respectively.
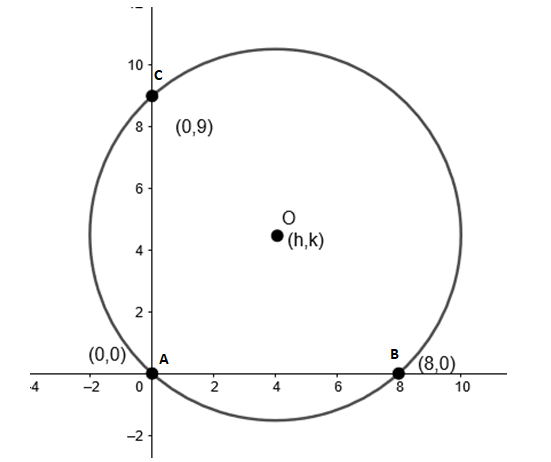
Let us assume that the center of the circle is at O.
Coordinates of O are (h, k).
Now, we know that the radius of the circle is of equal length. (Property of Circle)
We get, AO = BO = CO
AO, BO and CO are the radii of the circle, thus they are of equal length.
Also, from distance formula between two points, i.e. \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\]
\[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
where d is the distance between two points.
Applying this between AO and BO as both are the radii of the circle,
\[AO=BO\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( h \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{8}^{2}}-2\left( 8 \right)\left( h \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+64-16h}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+64-16h\]
Canceling the similar terms, from both sides, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 64-16h=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 16h=64\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{64}{16}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=4\]
Similarly, from AO = BO, we will again perform the same calculation for AO = CO.
We know that,
\[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Putting the values of AO and CO, we get
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-9 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( h \right)\left( 0 \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( h \right)\left( 0 \right)+{{k}^{2}}+81-2\left( 9 \right)\left( k \right)}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+81-18k}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+81-18k\]
Canceling equal terms from both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow 81-18k=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 18k=81\]
\[\Rightarrow k=\dfrac{81}{18}\]
\[k=4.5\]
Now, we are ready with our center coordinates.
\[h=4,\text{ }k=4.5\]
\[\left( h,k \right)=\left( 4,4.5 \right)\]
We know that radius of the circle \[=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\]
Putting the value of h and k, we get
\[=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4.5 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{16+20.25}\]
\[=\sqrt{36.25}\]
\[=6.042\]
Now, we are ready with all the required values to form an equation of the circle.
We know that the general equation of the circle is \[{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}\]
Substituting values of (h, k) and r in the general equation of the circle, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( x-4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-4.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 6.042 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+16-8x+{{y}^{2}}+20.25-9k=36.25\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-8x-9y=0\]
Thus, the required equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-8x-9y=0\]
Note: Alternate Method:
You can solve this question by using the following steps.
1. Substitute the values of the given point in the general equation of the circle.
2. Find the values of the unknowns i.e. (h, k) and r.
3. Form the required equation of the circle.
Distance Formula, \[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Given that we have to find the equation of a circle passing through points (0, 0), (8, 0) and (0, 9) respectively.

Let us assume that the center of the circle is at O.
Coordinates of O are (h, k).
Now, we know that the radius of the circle is of equal length. (Property of Circle)
We get, AO = BO = CO
AO, BO and CO are the radii of the circle, thus they are of equal length.
Also, from distance formula between two points, i.e. \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\]
\[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
where d is the distance between two points.
Applying this between AO and BO as both are the radii of the circle,
\[AO=BO\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-8 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( h \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{8}^{2}}-2\left( 8 \right)\left( h \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+64-16h}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+64-16h\]
Canceling the similar terms, from both sides, we get,
\[\Rightarrow 64-16h=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 16h=64\]
\[\Rightarrow h=\dfrac{64}{16}\]
\[\Rightarrow h=4\]
Similarly, from AO = BO, we will again perform the same calculation for AO = CO.
We know that,
\[d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}\]
Putting the values of AO and CO, we get
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-0 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{\left( h-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( k-9 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( h \right)\left( 0 \right)+{{k}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( 0 \right)\left( k \right)}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{0}^{2}}-2\left( h \right)\left( 0 \right)+{{k}^{2}}+81-2\left( 9 \right)\left( k \right)}\]
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+81-18k}\]
Squaring both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}={{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}+81-18k\]
Canceling equal terms from both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow 81-18k=0\]
\[\Rightarrow 18k=81\]
\[\Rightarrow k=\dfrac{81}{18}\]
\[k=4.5\]
Now, we are ready with our center coordinates.
\[h=4,\text{ }k=4.5\]
\[\left( h,k \right)=\left( 4,4.5 \right)\]
We know that radius of the circle \[=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\]
Putting the value of h and k, we get
\[=\sqrt{{{h}^{2}}+{{k}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{{{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4.5 \right)}^{2}}}\]
\[=\sqrt{16+20.25}\]
\[=\sqrt{36.25}\]
\[=6.042\]
Now, we are ready with all the required values to form an equation of the circle.
We know that the general equation of the circle is \[{{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{\left( r \right)}^{2}}\]
Substituting values of (h, k) and r in the general equation of the circle, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( x-4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-4.5 \right)}^{2}}={{\left( 6.042 \right)}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+16-8x+{{y}^{2}}+20.25-9k=36.25\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-8x-9y=0\]
Thus, the required equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-8x-9y=0\]
Note: Alternate Method:
You can solve this question by using the following steps.
1. Substitute the values of the given point in the general equation of the circle.
2. Find the values of the unknowns i.e. (h, k) and r.
3. Form the required equation of the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




