
Find the polar equation of a circle, the initial line being a tangent. What does it become if the origin is on the circumference?
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: To find the polar equation of a circle, we need to find the equation of the circle by considering angle as ‘m’ and radius as ‘a’ and then by using the polar coordinates of the circle, the polar equation can be calculated. Polar equation of a circle refers to the equation of circle expressed in polar coordinates, which includes angle of circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us construct a figure of a circle in the coordinate axis with a tangent along x – axis and radius ‘a’.
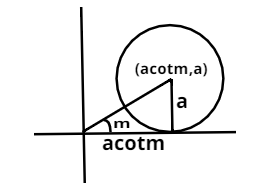
The angle subtended by the radius of the circle with the x – axis is ‘m’ as shown in the figure. Using this we can write the coordinates of the center of the circle (a cot m, a) from the figure.
In the circle we have assumed m as angle and the radius of circle is a. The circle is shown in the figure, equation of the circle will be
We know the equation of a circle is given by the formula, ${\left( {{\text{x - a}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{y - b}}} \right)^2} = {{\text{r}}^2}$, where (a, b) is the center of the circle and ‘r’ is the radius of the circle. Therefore,
${(x - a\cot m)^2} + {(y - a)^2} = {a^2}$ (Equation of circle)
Using the radius, we can write the x and y intercepts as r cosθ and r sinθ respectively. Here radius = a.
Converting it to polar form i.e. replacing x and y with $r\cos \theta $and$r\sin \theta $, we get
\[{(r\cos \theta - a\cot m)^2} + {(r\sin \theta - a)^2} = {a^2}\]
Opening the square we get,
\[
\Rightarrow {r^2}{\cos ^2}\theta + {a^2}{\cot ^2}m - 2ar\cos \theta \cot m + {r^2}{\sin ^2}\theta + {a^2} - 2ar\sin \theta = {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {r^2} + {a^2}{\cot ^2}m - 2r\cos \theta (a\cot m) - 2ar\sin \theta = 0 \\
\]
If the origin is on circumference, put $a\cot m = 0$ we get
$ \Rightarrow r = 2a\sin \theta $.
This is the required equation.
Note: In order to solve this type of questions the key is to just follow the steps of converting the normal coordinates to polar coordinates and making an appropriate construction to be able to solve the problem easily according to question and assigning out variables. We have to change it in polar form as done above.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us construct a figure of a circle in the coordinate axis with a tangent along x – axis and radius ‘a’.

The angle subtended by the radius of the circle with the x – axis is ‘m’ as shown in the figure. Using this we can write the coordinates of the center of the circle (a cot m, a) from the figure.
In the circle we have assumed m as angle and the radius of circle is a. The circle is shown in the figure, equation of the circle will be
We know the equation of a circle is given by the formula, ${\left( {{\text{x - a}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{y - b}}} \right)^2} = {{\text{r}}^2}$, where (a, b) is the center of the circle and ‘r’ is the radius of the circle. Therefore,
${(x - a\cot m)^2} + {(y - a)^2} = {a^2}$ (Equation of circle)
Using the radius, we can write the x and y intercepts as r cosθ and r sinθ respectively. Here radius = a.
Converting it to polar form i.e. replacing x and y with $r\cos \theta $and$r\sin \theta $, we get
\[{(r\cos \theta - a\cot m)^2} + {(r\sin \theta - a)^2} = {a^2}\]
Opening the square we get,
\[
\Rightarrow {r^2}{\cos ^2}\theta + {a^2}{\cot ^2}m - 2ar\cos \theta \cot m + {r^2}{\sin ^2}\theta + {a^2} - 2ar\sin \theta = {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {r^2} + {a^2}{\cot ^2}m - 2r\cos \theta (a\cot m) - 2ar\sin \theta = 0 \\
\]
If the origin is on circumference, put $a\cot m = 0$ we get
$ \Rightarrow r = 2a\sin \theta $.
This is the required equation.
Note: In order to solve this type of questions the key is to just follow the steps of converting the normal coordinates to polar coordinates and making an appropriate construction to be able to solve the problem easily according to question and assigning out variables. We have to change it in polar form as done above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




