
Find the sum of nodal plane of ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $anti-bonding molecular orbital.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The d-orbitals having four lobes overlap sidewise to form a pi bond. When these d-orbitals having four lobes overlap in a destructive manner, the ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $anti-bonding molecular orbital. The plane where the electron density is not found represents a node. By the picture of molecular orbitals, the nodal plane can be determined.
Complete Step by step answer: Two atomic orbital combines to form two molecular orbitals. Out of these two molecular orbital one is known as bonding which has low energy and the second is known as antibonding which has high energy. s-and one p-orbital forms sigma bond and remaining two p-orbitals form pi bonding.
The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{XZ}}$,${{\text{d}}_{YZ}}$, and${{\text{d}}_{XY}}$.
The structure of all five d-orbitals is represented as follows:
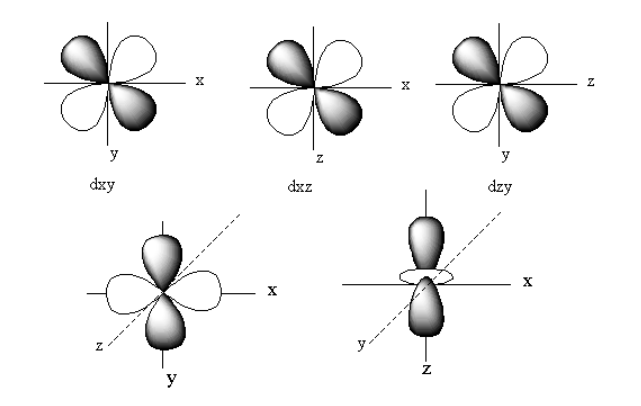
The pi bond is formed by side-on overlapping of the two d-orbitals. When two d-orbitals overlap out of phase the antibonding orbitals form. The antibonding molecular orbitals are denoted by superscript ‘$ * $’.
The structure of the bonding ${{{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}}$orbitals and ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding is as follows:
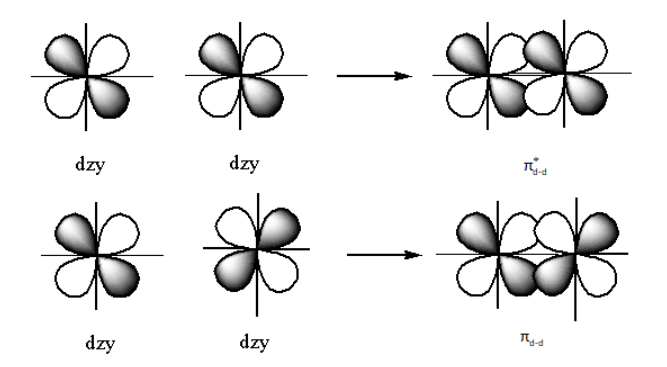
The nodal plane is the plane where the probability of finding the electrons is zero.
The nodal plane in ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding is as follows:
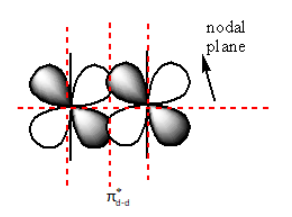
The red dashed lines in the above diagram show the nodal plane. So, the ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding molecular orbitals have a total of four nodal planes.
Therefore, the sum of the nodal plane of ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $anti-bonding molecular orbital is four.
Note: At node the sign of orbital changes. Here, the dark colour and light colour of the orbitals shows the different phases of the orbitals. So, the change of colour (dark to light or light to dark) shows the phase change. Pi bonding orbitals form by constructive overlapping of the two d-orbitals. The nodal plane in pi bonding ${{{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}}$ molecular orbital is three.
Complete Step by step answer: Two atomic orbital combines to form two molecular orbitals. Out of these two molecular orbital one is known as bonding which has low energy and the second is known as antibonding which has high energy. s-and one p-orbital forms sigma bond and remaining two p-orbitals form pi bonding.
The d-orbital is a set of five denigrate orbitals named as ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{z}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{{{\text{X}}^2} - {{\text{Y}}^{\text{2}}}}}$, ${{\text{d}}_{XZ}}$,${{\text{d}}_{YZ}}$, and${{\text{d}}_{XY}}$.
The structure of all five d-orbitals is represented as follows:

The pi bond is formed by side-on overlapping of the two d-orbitals. When two d-orbitals overlap out of phase the antibonding orbitals form. The antibonding molecular orbitals are denoted by superscript ‘$ * $’.
The structure of the bonding ${{{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}}$orbitals and ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding is as follows:

The nodal plane is the plane where the probability of finding the electrons is zero.
The nodal plane in ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding is as follows:

The red dashed lines in the above diagram show the nodal plane. So, the ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $ anti-bonding molecular orbitals have a total of four nodal planes.
Therefore, the sum of the nodal plane of ${{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}^ * $anti-bonding molecular orbital is four.
Note: At node the sign of orbital changes. Here, the dark colour and light colour of the orbitals shows the different phases of the orbitals. So, the change of colour (dark to light or light to dark) shows the phase change. Pi bonding orbitals form by constructive overlapping of the two d-orbitals. The nodal plane in pi bonding ${{{\pi }}_{{\text{d - d}}}}$ molecular orbital is three.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




