
Find the value of $ \cos 120{}^\circ $.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: In a right-angled triangle with the length of the side opposite to angle θ as perpendicular (P), base (B) and hypotenuse (H):
$ \sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H},\cos \theta =\dfrac{B}{H},\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B} $
$ {{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}={{H}^{2}} $ (Pythagoras' Theorem)
If a point P is at a distance $ r $ from the origin, then the coordinates of the point are $ \left( r\cos \theta,r\sin \theta \right) $, where $ \theta $ is angle made by line OP with the positive direction of the x-axis.
Find the coordinates of a point which is 1 unit far from the origin and makes an angle of $ 120{}^\circ $ with the x-axis. The x-co-ordinate of the point is the value of $ \cos 120{}^\circ $.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us mark a point P on the graph paper, at distance of 1 unit from the origin, such that OP makes an angle of $ 120{}^\circ $ with the positive direction of the x-axis.
From the definition of trigonometric ratios, we know that the x-co-ordinate of the point P is the value of $ \cos 120{}^\circ $ and the y-coordinate is the value of $ \sin 120{}^\circ $.
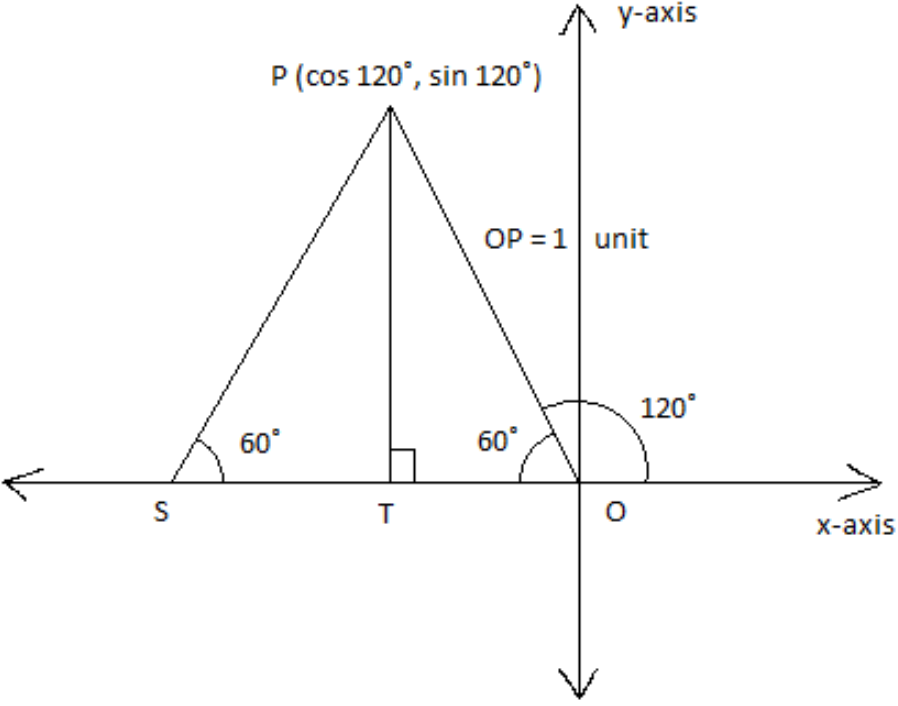
The $ \Delta PSO $ in the above diagram is an equilateral triangle.
∴ $ OP=OS=1 $ ... (1)
Also, $ \Delta PTO\cong \Delta PTS $ ... (Using ASA congruence)
∴ $ ST=OT=\dfrac{1}{2}OS $
⇒ $ OT=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1=\dfrac{1}{2} $ ... [Using equation (1)]
It means that the coordinates of the point T are $ \left( -\dfrac{1}{2},0 \right) $.
Since the point P is on the perpendicular line at point T, its x-co-ordinate must also be the same as that of T, i.e. $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $.
It follows that $ \cos 120{}^\circ =-\dfrac{1}{2} $.
Note: Now that we know the lengths of OP and OT, we can use Pythagoras' theorem and find PT as well, which is the y-coordinate of P, i.e. $ \sin 120{}^\circ $.
Rule of CAST: In the IV, I, II and III quadrants, $ \cos \theta $, All trigonometric ratios, $ \sin \theta $ and $ \tan \theta $ are positive, respectively.
Trigonometric Ratios for Allied Angles:
$ \sin \left( -\theta \right)=-\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left( 2n\pi +\theta \right)=\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( 2n\pi +\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left( n\pi +\theta \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{n}}\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( n\pi +\theta \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{n}}\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left[ (2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\theta \right]={{(-1)}^{n}}\cos \theta $ $ \cos \left[ (2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\theta \right]={{(-1)}^{n}}\left( -\sin \theta \right) $
If one trigonometric ratio is known, we can use Pythagoras' Theorem and calculate the values of all other trigonometric ratios.
$ \sin \theta =\dfrac{P}{H},\cos \theta =\dfrac{B}{H},\tan \theta =\dfrac{P}{B} $
$ {{P}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}={{H}^{2}} $ (Pythagoras' Theorem)
If a point P is at a distance $ r $ from the origin, then the coordinates of the point are $ \left( r\cos \theta,r\sin \theta \right) $, where $ \theta $ is angle made by line OP with the positive direction of the x-axis.
Find the coordinates of a point which is 1 unit far from the origin and makes an angle of $ 120{}^\circ $ with the x-axis. The x-co-ordinate of the point is the value of $ \cos 120{}^\circ $.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us mark a point P on the graph paper, at distance of 1 unit from the origin, such that OP makes an angle of $ 120{}^\circ $ with the positive direction of the x-axis.
From the definition of trigonometric ratios, we know that the x-co-ordinate of the point P is the value of $ \cos 120{}^\circ $ and the y-coordinate is the value of $ \sin 120{}^\circ $.

The $ \Delta PSO $ in the above diagram is an equilateral triangle.
∴ $ OP=OS=1 $ ... (1)
Also, $ \Delta PTO\cong \Delta PTS $ ... (Using ASA congruence)
∴ $ ST=OT=\dfrac{1}{2}OS $
⇒ $ OT=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 1=\dfrac{1}{2} $ ... [Using equation (1)]
It means that the coordinates of the point T are $ \left( -\dfrac{1}{2},0 \right) $.
Since the point P is on the perpendicular line at point T, its x-co-ordinate must also be the same as that of T, i.e. $ -\dfrac{1}{2} $.
It follows that $ \cos 120{}^\circ =-\dfrac{1}{2} $.
Note: Now that we know the lengths of OP and OT, we can use Pythagoras' theorem and find PT as well, which is the y-coordinate of P, i.e. $ \sin 120{}^\circ $.
Rule of CAST: In the IV, I, II and III quadrants, $ \cos \theta $, All trigonometric ratios, $ \sin \theta $ and $ \tan \theta $ are positive, respectively.
Trigonometric Ratios for Allied Angles:
$ \sin \left( -\theta \right)=-\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left( 2n\pi +\theta \right)=\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( 2n\pi +\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left( n\pi +\theta \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{n}}\sin \theta $ $ \cos \left( n\pi +\theta \right)={{\left( -1 \right)}^{n}}\cos \theta $
$ \sin \left[ (2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\theta \right]={{(-1)}^{n}}\cos \theta $ $ \cos \left[ (2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\theta \right]={{(-1)}^{n}}\left( -\sin \theta \right) $
If one trigonometric ratio is known, we can use Pythagoras' Theorem and calculate the values of all other trigonometric ratios.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




