
How to find which compound is dextro and laevo rotatory from its structure?
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: If an organic compound is asymmetric and consists of at least one chiral carbon, then that compound is known as an optically active compound. The major conditions for a compound to be optically active are:
-There should be no plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry in the compound.
-The compound must have a chiral plane.
Complete answer:
When a compound is optically active, then it has the ability to rotate the plane of polarized light to two directions i.e., either left or right.
In general, ordinary light is formed from electromagnetic waves of different wavelength whereas the monochromatic light consists of only one wavelength. Plane of polarized light is an example of monochromatic light. Therefore, the compounds which are asymmetrical in nature, can rotate the plane of polarized light.
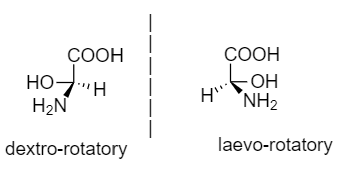
Dextro-rotatory compound: The compounds which rotate the plane of polarized light to the right or clockwise, then it is said to be dextro-rotatory.
Laevo-rotatory compound: The compound which rotates the plane of polarized light to the left or anticlockwise, then it is said to be laevo-rotatory.
An example for dextro and laevo rotatory compounds is given below:
Note:
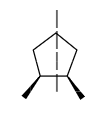
If a compound that has a chiral carbon but consists of a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry, then it is known as a meso compound. These compounds are optically inactive but they can have absolute configuration for the chiral carbon present in the compound.
Example for meso compound is given below.
-There should be no plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry in the compound.
-The compound must have a chiral plane.
Complete answer:
When a compound is optically active, then it has the ability to rotate the plane of polarized light to two directions i.e., either left or right.
In general, ordinary light is formed from electromagnetic waves of different wavelength whereas the monochromatic light consists of only one wavelength. Plane of polarized light is an example of monochromatic light. Therefore, the compounds which are asymmetrical in nature, can rotate the plane of polarized light.
Dextro-rotatory compound: The compounds which rotate the plane of polarized light to the right or clockwise, then it is said to be dextro-rotatory.
Laevo-rotatory compound: The compound which rotates the plane of polarized light to the left or anticlockwise, then it is said to be laevo-rotatory.
An example for dextro and laevo rotatory compounds is given below:

Note:
If a compound that has a chiral carbon but consists of a plane of symmetry or centre of symmetry, then it is known as a meso compound. These compounds are optically inactive but they can have absolute configuration for the chiral carbon present in the compound.
Example for meso compound is given below.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




