
Fluorobenzene\[({C_6}{H_5}F)\] can be synthesized in the laboratory:
(A) By heating phenol with \[HF\] and \[KF\]
(B) From aniline by diazotization followed by heating the diazonium salt with \[HB{F_4}\].
(C) By direct fluorination of benzene with \[{F_2}\] gas
(D) By reacting bromobenzene with \[NaF\] solution
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: As we know that the fluorine atom is very small in size and also is an electron rich atom and\[{F_2}\] gas is very explosive in nature so if we use fluorine atom in direct substitution it could be very harmful in laboratory.
Complete step by step answer:
If we use fluorine gas directly it can be very explosive due to its very small size and more electrons around the fluorine nucleus.
So in laboratory we synthesis \[({C_6}{H_5}F)\] indirectly, which is known as Balz-Schiemann reaction in which we will take aniline as a substrate which will react with \[HN{O_2}\] (nitrous acid) in the presence of fluoroboric acid and gives a product diazonium salt. As the diazo group is a good leaving group so by reacting diazo-benzene with \[HB{F_4}\],this fluoroboric acid attacks the diazo group and replaces diazo with fluorine atom. The \[HB{F_4}\] gives fluoride ion as a nucleophile which attacks on diazo group. So the final product we will get as \[({C_6}{H_5}F)\].
The mechanism is shown as below.
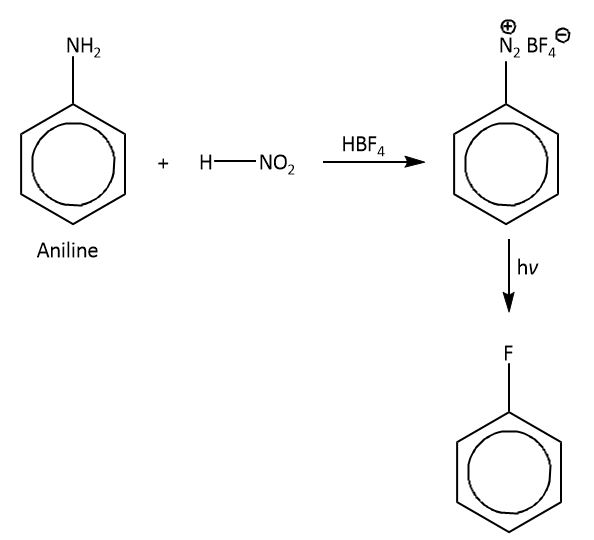
Therefore, the correct option is option (B).
Note:
Diazotization can also occur in the presence of other acids such as sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid.
Complete step by step answer:
If we use fluorine gas directly it can be very explosive due to its very small size and more electrons around the fluorine nucleus.
So in laboratory we synthesis \[({C_6}{H_5}F)\] indirectly, which is known as Balz-Schiemann reaction in which we will take aniline as a substrate which will react with \[HN{O_2}\] (nitrous acid) in the presence of fluoroboric acid and gives a product diazonium salt. As the diazo group is a good leaving group so by reacting diazo-benzene with \[HB{F_4}\],this fluoroboric acid attacks the diazo group and replaces diazo with fluorine atom. The \[HB{F_4}\] gives fluoride ion as a nucleophile which attacks on diazo group. So the final product we will get as \[({C_6}{H_5}F)\].
The mechanism is shown as below.

Therefore, the correct option is option (B).
Note:
Diazotization can also occur in the presence of other acids such as sulphuric acid, hydrochloric acid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




