
Following configuration of the tartaric acid represents
A. $2R,3R$
B. $2R,3S$
C. $2S,3S$
D. $2S,3R$

Answer
567k+ views
Hint: Cahn Ingold Prelog (C.I.P) priority rules are used to determine the R and S configuration of a molecule. Taking the priority of the groups we can determine the configuration of the molecule.
Method to assign R and S rotation
Identify the number of stereo-centers in the molecule.Identify the four different ligands attached to each of the stereo-centers.Assign to each of the substituents as priority symbols based on the sequence rule$A > B > C > D$. The atom whose atomic number is more will get the priority.If the first atom of the ligand is the same or has the same atomic number then we will see the second molecule and if there is a change in the atomic number of the second molecule then the second molecule with a higher atomic number will get the priority. The molecule is then viewed through a hypothetical path moving from$A \to B \to C \to D$. If this path describes a clockwise direction then the structure is said to have R-configuration and if the path describes an anti-clockwise direction then the structure is said to have S-configuration. The least priority i.e. hydrogen should lie below the plane. If the least priority group is above the plane there is a change in configuration i.e. $R \to S$ and $S \to R$.
Complete step by step answer:
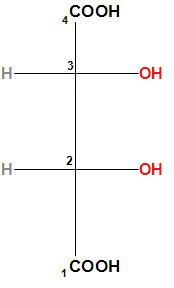
The given structure of the tartaric acid is:
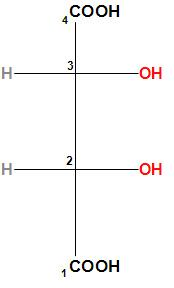
Let us first find the configuration of the second carbon. The –OH group will get the priority (as oxygen atomic number is more than carbon), the –COOH group will get second priority, the third carbon will get the third priority (as the third carbon is linked with a C, O, and H) and the hydrogen will get the least priority. In the below structure we can understand it clearly.
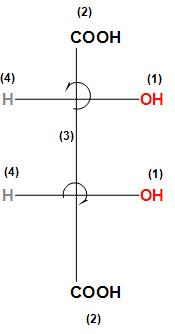
Therefore we can see that the hypothetical path describes a clockwise path for second carbon so it will be R but the least priority group i.e. hydrogen is not below plane so there will be a change in configuration $R \to S$ so the final configuration will be S-configuration.
Similarly, for the third carbon the –OH group is taken as a priority, the –COOH is taken as a second priority, the second carbon is taken as a third priority (as the second carbon is linked with C, O, and H atoms) and the hydrogen is taken as least priority. As we can see that the hypothetical path describes an anti-clockwise path so it will be S-configuration but the least priority group i.e. hydrogen is not below the plane so there will be a change in configuration $S \to R$ so the final configuration will be R-configuration.
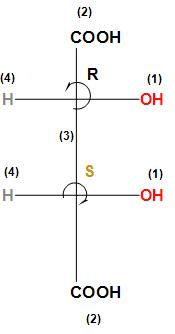
After discussing we can conclude that given tartaric acid which a Meso compound has a configuration $2S,3R$.
So, the correct answer is Option D .
Note: If a molecule is optically inactive despite the presence of multiple chiral centers, then the molecule is said to be meso- compound. For example, in the given structure of meso- tartaric acid, if a plane of symmetry passes through the middle of the molecule, the positive rotation of one part of the molecule is multiplied by the negative rotation of the other part of the molecule within the same molecule i.e. internal compensation.
Method to assign R and S rotation
Identify the number of stereo-centers in the molecule.Identify the four different ligands attached to each of the stereo-centers.Assign to each of the substituents as priority symbols based on the sequence rule$A > B > C > D$. The atom whose atomic number is more will get the priority.If the first atom of the ligand is the same or has the same atomic number then we will see the second molecule and if there is a change in the atomic number of the second molecule then the second molecule with a higher atomic number will get the priority. The molecule is then viewed through a hypothetical path moving from$A \to B \to C \to D$. If this path describes a clockwise direction then the structure is said to have R-configuration and if the path describes an anti-clockwise direction then the structure is said to have S-configuration. The least priority i.e. hydrogen should lie below the plane. If the least priority group is above the plane there is a change in configuration i.e. $R \to S$ and $S \to R$.
Complete step by step answer:
The given structure of the tartaric acid is:

Let us first find the configuration of the second carbon. The –OH group will get the priority (as oxygen atomic number is more than carbon), the –COOH group will get second priority, the third carbon will get the third priority (as the third carbon is linked with a C, O, and H) and the hydrogen will get the least priority. In the below structure we can understand it clearly.

Therefore we can see that the hypothetical path describes a clockwise path for second carbon so it will be R but the least priority group i.e. hydrogen is not below plane so there will be a change in configuration $R \to S$ so the final configuration will be S-configuration.
Similarly, for the third carbon the –OH group is taken as a priority, the –COOH is taken as a second priority, the second carbon is taken as a third priority (as the second carbon is linked with C, O, and H atoms) and the hydrogen is taken as least priority. As we can see that the hypothetical path describes an anti-clockwise path so it will be S-configuration but the least priority group i.e. hydrogen is not below the plane so there will be a change in configuration $S \to R$ so the final configuration will be R-configuration.

After discussing we can conclude that given tartaric acid which a Meso compound has a configuration $2S,3R$.
So, the correct answer is Option D .
Note: If a molecule is optically inactive despite the presence of multiple chiral centers, then the molecule is said to be meso- compound. For example, in the given structure of meso- tartaric acid, if a plane of symmetry passes through the middle of the molecule, the positive rotation of one part of the molecule is multiplied by the negative rotation of the other part of the molecule within the same molecule i.e. internal compensation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




