
How do the following react?
(i) Benzyl phenyl ether and HI at 375 K.
(ii) Ethyl methyl ether and ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ at 273 K.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Ethers can be defined as a group of organic compounds having an oxygen atom which is further bonded to two same or different alkyl or aryl groups. The general formula represented by ethers is R-O-R’, where R and R’ represents any alkyl group or aryl group both may or may not be the same.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss both the reactions one by one
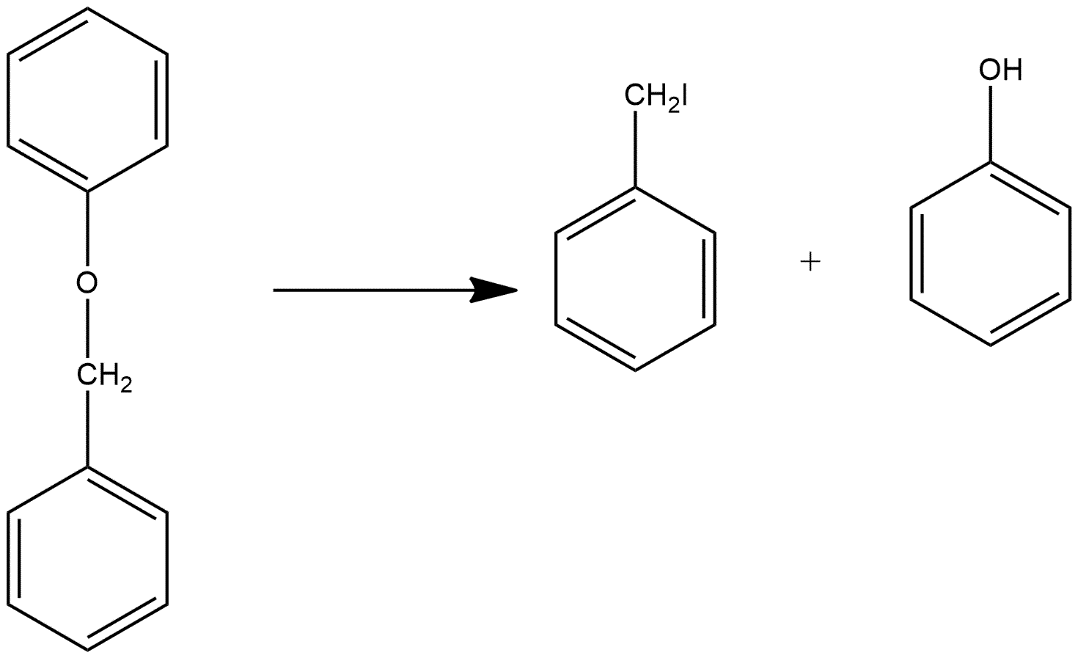
(i) Benzyl phenyl ether is shown by R-O-R’ in which one R group is benzyl and R’ group is represented by benzyl group and the structure is shown as:

When benzyl phenyl ether reacts with HI it gives benzyl iodide and phenol as products and reaction can be shown as:
(ii) Ethyl methyl ether in which one substituent is ethyl and another one is methyl and both are attached with oxygen atom which can be shown as:
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}$ reacts with sulfuric acid i.e. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ reacts with ethyl methyl ether then ethers are hydrolyzed into alcohols which can be shown as:
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}OH$
Product formed are methanol and ethanol.
Note:
On the basic R and R’ group attached to oxygen atom ethers are divided into two categories that are known as symmetrical and asymmetrical ethers in which symmetrical ethers have two identical groups attached to either side of an oxygen atom while in case of unsymmetrical ethers there are two distinct group attached to either side of an oxygen atom.
Complete answer:
Let’s discuss both the reactions one by one
(i) Benzyl phenyl ether is shown by R-O-R’ in which one R group is benzyl and R’ group is represented by benzyl group and the structure is shown as:

When benzyl phenyl ether reacts with HI it gives benzyl iodide and phenol as products and reaction can be shown as:

(ii) Ethyl methyl ether in which one substituent is ethyl and another one is methyl and both are attached with oxygen atom which can be shown as:
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}$ reacts with sulfuric acid i.e. ${{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}$ reacts with ethyl methyl ether then ethers are hydrolyzed into alcohols which can be shown as:
${{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OC{{H}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to {{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}}OH+C{{H}_{3}}OH$
Product formed are methanol and ethanol.
Note:
On the basic R and R’ group attached to oxygen atom ethers are divided into two categories that are known as symmetrical and asymmetrical ethers in which symmetrical ethers have two identical groups attached to either side of an oxygen atom while in case of unsymmetrical ethers there are two distinct group attached to either side of an oxygen atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




