
For a diode connected in parallel with a resistor, which is the most likely current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic?
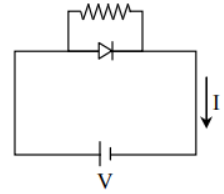
A.
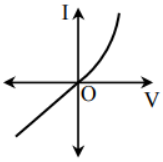
B.
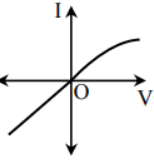
C.
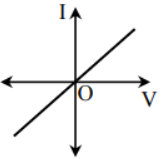
D.





Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: The current always follows the path where resistance is minimum. The diode only conducts forward biasing. The diode doesn’t work in reverse bias.
Complete step by step answer:
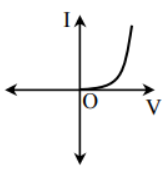
You have to find the I – V characteristic of the given circuit.
Notice the question, the resistance is connected in parallel with the diode. So, when the diode is forward biased, the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode dominant. Or when the diode in reverse bias then, current passes through the resistance then, the current (I) is directly proportional to the voltage (V).
The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic in option A fits the most.
So, option A is the correct answer.
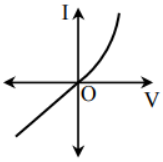
Option B is incorrect because on the positive side the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is wrong.
Option C is incorrect because on the positive side the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is wrong.
Option D is incorrect because when the diode is reverse biased then the current is directly proportional to the voltage. This part of the graph had not been drawn.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
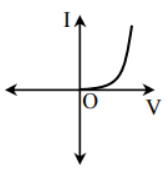
For the diode in forward bias, the current increases exponentially with the voltage, and in reverse bias, the ideal diode does not conduct any current through the diode.
The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is.
The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the resistor is
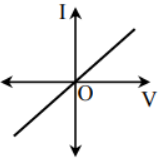
The current is directly proportional to the voltage for the resistor.
Note:
Try to remember the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode. In forward bias, the current increases exponentially with the voltage. And in reverse bias the ideal diode does not conduct any current through the diode.
Complete step by step answer:
You have to find the I – V characteristic of the given circuit.
Notice the question, the resistance is connected in parallel with the diode. So, when the diode is forward biased, the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode dominant. Or when the diode in reverse bias then, current passes through the resistance then, the current (I) is directly proportional to the voltage (V).
The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic in option A fits the most.
So, option A is the correct answer.

Option B is incorrect because on the positive side the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is wrong.
Option C is incorrect because on the positive side the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is wrong.
Option D is incorrect because when the diode is reverse biased then the current is directly proportional to the voltage. This part of the graph had not been drawn.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Additional Information:
For the diode in forward bias, the current increases exponentially with the voltage, and in reverse bias, the ideal diode does not conduct any current through the diode.
The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode is.

The current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the resistor is

The current is directly proportional to the voltage for the resistor.
Note:
Try to remember the current (I) – voltage (V) characteristic of the diode. In forward bias, the current increases exponentially with the voltage. And in reverse bias the ideal diode does not conduct any current through the diode.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




