
For a transistor amplifier, the voltage gain
A. Remains constant for all frequencies
B. Is high at low and high frequencies and constant in the middle range frequencies.
C. Is low at low and high frequencies and constant in the middle range frequencies.
D. None of the above.
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Recall the circuit diagram for the transistor working as an amplifier. We know that capacitors oppose the current flow. Recall the formula for reactance of the capacitor and use this formula to answer this question.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a transistor is used for increasing the amplitude of the alternating signal. We can draw the amplifier circuit as an amplifier.
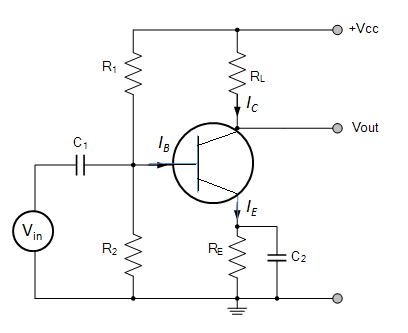
We know that the voltage gain is defined as the ratio of change in output voltage to the change in input voltage. The voltage gain of the transistor amplifier is given as,
\[{A_v} = \dfrac{{\Delta {V_O}}}{{\Delta {V_I}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[\Delta {V_O}\] is the change in output voltage and \[\Delta {V_I}\] is the change in input voltage.
We know that the voltage gain of the amplifier changes with frequency because the reactance of the coupling capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] changes with frequency as per the following equation.
\[{X_C} = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi fC}}\]
Here, f is the frequency and C is the capacitance.
At low frequencies, the reactance \[{X_C}\] of the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] becomes high. Therefore, the output signal flowing through the capacitor decreases effectively. Since the output voltage decreases, from equation (1), the voltage gain also decreases at low frequencies.
At high frequencies, the reactance of the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] becomes low, and it will allow the maximum flow of signal through it. But this will increase the loading effect of the amplifier and eventually the transistor starts to reduce the signal. Also, at high frequencies, the reactance of the coupling capacitor \[{C_1}\] is very small. Therefore, the base current will increase. We know the relation, the current amplification factor \[\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}}\], where, \[{I_C}\] is the collector current and \[{I_B}\] is the base current. When the base current increases the amplification factor decreases. Therefore, the voltage gain of the transistor amplifier decreases at high frequencies.
At mid range frequencies, the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] provides constant reactance and in turn, the voltage gain remains constant.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
To answer these types of questions, students should remember the formula for voltage gain, reactance of capacitor and current amplification factor. Most of the time, such types of questions can be answered at the first glance at the proper formula. In the circuit diagram, \[{V_{in}}\] is the AC supply whereas \[{V_{CC}}\] is the DC supply. Note that capacitors oppose only AC signals and not DC signals.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a transistor is used for increasing the amplitude of the alternating signal. We can draw the amplifier circuit as an amplifier.

We know that the voltage gain is defined as the ratio of change in output voltage to the change in input voltage. The voltage gain of the transistor amplifier is given as,
\[{A_v} = \dfrac{{\Delta {V_O}}}{{\Delta {V_I}}}\] …… (1)
Here, \[\Delta {V_O}\] is the change in output voltage and \[\Delta {V_I}\] is the change in input voltage.
We know that the voltage gain of the amplifier changes with frequency because the reactance of the coupling capacitors \[{C_1}\] and \[{C_2}\] changes with frequency as per the following equation.
\[{X_C} = \dfrac{1}{{2\pi fC}}\]
Here, f is the frequency and C is the capacitance.
At low frequencies, the reactance \[{X_C}\] of the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] becomes high. Therefore, the output signal flowing through the capacitor decreases effectively. Since the output voltage decreases, from equation (1), the voltage gain also decreases at low frequencies.
At high frequencies, the reactance of the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] becomes low, and it will allow the maximum flow of signal through it. But this will increase the loading effect of the amplifier and eventually the transistor starts to reduce the signal. Also, at high frequencies, the reactance of the coupling capacitor \[{C_1}\] is very small. Therefore, the base current will increase. We know the relation, the current amplification factor \[\beta = \dfrac{{{I_C}}}{{{I_B}}}\], where, \[{I_C}\] is the collector current and \[{I_B}\] is the base current. When the base current increases the amplification factor decreases. Therefore, the voltage gain of the transistor amplifier decreases at high frequencies.
At mid range frequencies, the coupling capacitor \[{C_2}\] provides constant reactance and in turn, the voltage gain remains constant.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
To answer these types of questions, students should remember the formula for voltage gain, reactance of capacitor and current amplification factor. Most of the time, such types of questions can be answered at the first glance at the proper formula. In the circuit diagram, \[{V_{in}}\] is the AC supply whereas \[{V_{CC}}\] is the DC supply. Note that capacitors oppose only AC signals and not DC signals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




