
Four charges are arranged at the corners of a square ABCD as shown in figure. The force on a positive charge kept at the centre of the square is:
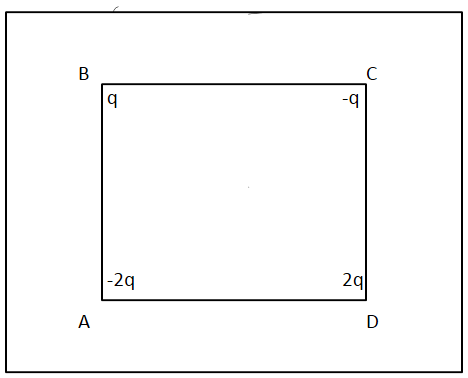
(A) Zero
(B) Along diagonal AC
(C) Along diagonal BD
(D) Perpendicular to side AB

Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: The charge at the centre is positive, hence the positive charges placed at different corners will repel the charge at centre, whereas negative charges will attract the charge at centre. And since the charge at centre is equidistant from all the charges, the force applied by each charge will be proportional to the magnitude of the charge applying that force.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the diagram with a positive charge, say +Q, placed at the centre.
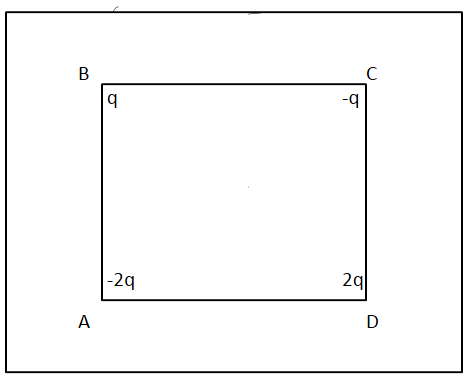
The charge at B is q, since it is a positive charge it will repel the charge at centre with force, say, F.
The charge at C is –q, since it is a negative charge it will attract the charge at centre with force F.
The charge at D is 2q, since it is a positive charge it will repel the charge at centre with force 2F.
The charge at A is –2q, since it is a negative charge it will attract the charge at centre with force 2F.
So the charge at the centre will experience the following forces,
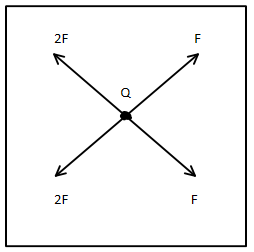
Solving the forces in opposite direction, we get
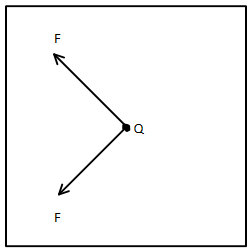
The resultant of these forces can be calculated by
\[R = \sqrt {{F^2} + {F^2}} \]
$R = F\sqrt[{}]{2}$
Since both the forces in the above diagram are equal in magnitude, the resultant force will be as shown below
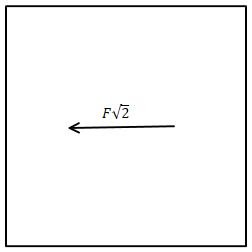
Hence the resultant force on charge at centre will be towards side AB and perpendicular to AB
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Before solving the problem, the student needs to be able to understand the coulomb’s law and the attraction and repulsion property of charges. A general mistake that students make while solving such questions is going into calculations. Since the question only demands the direction of the force, calculation of magnitude is a time wasting exercise, which one should avoid.
Complete step by step solution:
Consider the diagram with a positive charge, say +Q, placed at the centre.

The charge at B is q, since it is a positive charge it will repel the charge at centre with force, say, F.
The charge at C is –q, since it is a negative charge it will attract the charge at centre with force F.
The charge at D is 2q, since it is a positive charge it will repel the charge at centre with force 2F.
The charge at A is –2q, since it is a negative charge it will attract the charge at centre with force 2F.
So the charge at the centre will experience the following forces,

Solving the forces in opposite direction, we get

The resultant of these forces can be calculated by
\[R = \sqrt {{F^2} + {F^2}} \]
$R = F\sqrt[{}]{2}$
Since both the forces in the above diagram are equal in magnitude, the resultant force will be as shown below

Hence the resultant force on charge at centre will be towards side AB and perpendicular to AB
Therefore, the correct answer is option (D).
Note: Before solving the problem, the student needs to be able to understand the coulomb’s law and the attraction and repulsion property of charges. A general mistake that students make while solving such questions is going into calculations. Since the question only demands the direction of the force, calculation of magnitude is a time wasting exercise, which one should avoid.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




