
Free-central placentation is seen in
(a)Brassica
(b)Citrus
(c)Dianthus
(d)Argemone
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: A flower belonging to the family Caryophyllaceae with the flowers having five petals, typically with a frilled or pinked margin. It is observed in Primrose.
Complete answer:
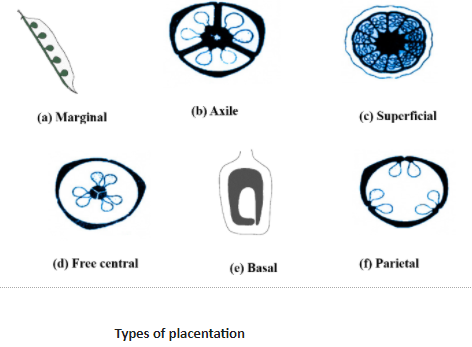
In plants, placentation is the attachment of ovules inside the ovary of the flower. The part of the ovary where the ovule is attached is referred to as the placenta hence the arrangement is referred to as placentation. In free central placentation, a unilocular ovary is seen and ovules are arranged on the central axis. This is seen in the dianthus.
Additional Information: -The term placentation means the formation, arrangement, and structure, of the placenta of an organism along with its type.
-The nutrients, water, and respiratory gases as well as the removal of excretory wastes are exchanged and moved between the body of the mother and fetus is done by placental tissues.
-Placentation types in flowering plants include:
Basal: The placenta is found in all syncarpous ovaries. In this single ovule is attached at the base (bottom) of the ovary. E.g.: Sunflower
Parietal: It is found in a multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Unilocular ovary becomes bilocular and ovules attach to the margin .E.g.: Cucumber, Argemone
Axile: It is also found in a multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The ovules are arranged on the axis like the placenta. E.g.: Citrus fruits, Brassica
Free central: It is found in a syncarpous ovary. The unilocular condition of the ovary is formed and ovules are arranged on the central axis. E.g.: Dianthus, primroses
Marginal: It is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary, the placenta forms a rigid along ventral side, and ovules are arranged in two vertical rows. E.g.: pea
So, the correct answer is ‘Dianthus’.
Note: The name Dianthus is derived from the Greek words Dios ("of Zeus") and anthos ("flower"), and was cited by the Greek botanist Theophrastus. The placentation occurs mostly in syncarpous ovaries, where carpels have fused and appeared as one carpel, but when you cut it open you can see there is more than one ovary.
Complete answer:
In plants, placentation is the attachment of ovules inside the ovary of the flower. The part of the ovary where the ovule is attached is referred to as the placenta hence the arrangement is referred to as placentation. In free central placentation, a unilocular ovary is seen and ovules are arranged on the central axis. This is seen in the dianthus.
Additional Information: -The term placentation means the formation, arrangement, and structure, of the placenta of an organism along with its type.
-The nutrients, water, and respiratory gases as well as the removal of excretory wastes are exchanged and moved between the body of the mother and fetus is done by placental tissues.
-Placentation types in flowering plants include:
Basal: The placenta is found in all syncarpous ovaries. In this single ovule is attached at the base (bottom) of the ovary. E.g.: Sunflower
Parietal: It is found in a multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. Unilocular ovary becomes bilocular and ovules attach to the margin .E.g.: Cucumber, Argemone
Axile: It is also found in a multicarpellary syncarpous ovary. The ovules are arranged on the axis like the placenta. E.g.: Citrus fruits, Brassica
Free central: It is found in a syncarpous ovary. The unilocular condition of the ovary is formed and ovules are arranged on the central axis. E.g.: Dianthus, primroses
Marginal: It is found in the monocarpellary unilocular ovary, the placenta forms a rigid along ventral side, and ovules are arranged in two vertical rows. E.g.: pea
So, the correct answer is ‘Dianthus’.

Note: The name Dianthus is derived from the Greek words Dios ("of Zeus") and anthos ("flower"), and was cited by the Greek botanist Theophrastus. The placentation occurs mostly in syncarpous ovaries, where carpels have fused and appeared as one carpel, but when you cut it open you can see there is more than one ovary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




