
From below what are the properties of concave mirrors?
A. Converging mirrors and forming a real and inverted image in front of the mirror.
B. Diverging mirrors and forming a virtual and upright image behind the mirror.
C. Converging mirrors and forming virtual and inverted images in front of the mirror.
D. Diverging mirrors form real and inverted images in front of the mirror.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint - The concave mirror, or converging mirror, has a reflecting surface which is recessed inward (away from the incident light). Concave mirrors reflect light inward to a single focal point. They 're used to concentrating on color. Knowing this will help you find the properties of the concave mirror and show you the answers.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The concave mirror image can be drawn as:
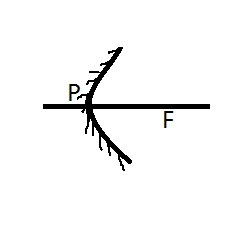
P is the mirror pole. F is the mirror 's focus. PF is the focal length f and the radius of the circle the mirror component of which is R = 2f.
A concave mirror is a type of mirror that is bent inward in the middle. In addition, if you look in this mirror, you'll feel like you're looking in a cave. In addition, we use a mirror equation to deal with a concave mirror.
Concave mirrors are converging mirrors, i.e. light rays on them converge. The concave mirror image may be either actual and inverted in front of the mirror or simulated and upright behind the mirror.
We know from the above knowledge that the appropriate choice is A.
Note - The mirror is an object that reflects the light in the same angle that it receives from the source. In fact, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection in the mirror. In fact, the reflected light is of the same intensity as the projected sun. There are three types of smooth, concave and convex mirrors. The equation for such mirrors specifies how far or close the object is from the mirror and what the size of the object is (large or small). In fact, the law of reflection also functions on the surface of a concave mirror. The angle of incidence in the concave mirror, however, is not equal to the angle of reflection.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The concave mirror image can be drawn as:

P is the mirror pole. F is the mirror 's focus. PF is the focal length f and the radius of the circle the mirror component of which is R = 2f.
A concave mirror is a type of mirror that is bent inward in the middle. In addition, if you look in this mirror, you'll feel like you're looking in a cave. In addition, we use a mirror equation to deal with a concave mirror.
Concave mirrors are converging mirrors, i.e. light rays on them converge. The concave mirror image may be either actual and inverted in front of the mirror or simulated and upright behind the mirror.
We know from the above knowledge that the appropriate choice is A.
Note - The mirror is an object that reflects the light in the same angle that it receives from the source. In fact, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection in the mirror. In fact, the reflected light is of the same intensity as the projected sun. There are three types of smooth, concave and convex mirrors. The equation for such mirrors specifies how far or close the object is from the mirror and what the size of the object is (large or small). In fact, the law of reflection also functions on the surface of a concave mirror. The angle of incidence in the concave mirror, however, is not equal to the angle of reflection.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




