
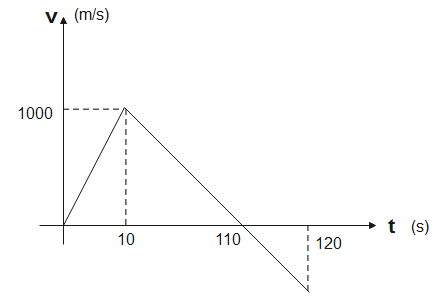
From the velocity-time graph of a rocket the maximum height attained by the rocket in $km$ is-

Answer
564.3k+ views
Hint: Rocket has maximum kinetic energy when it attains maximum velocity. By the law of conservation of mechanical energy, maximum kinetic energy=maximum potential energy. Substituting corresponding values, we can calculate maximum height. Convert between units as required.
Formula Used:
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mgh$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Velocity is defined as the displacement covered in unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-1}}$.
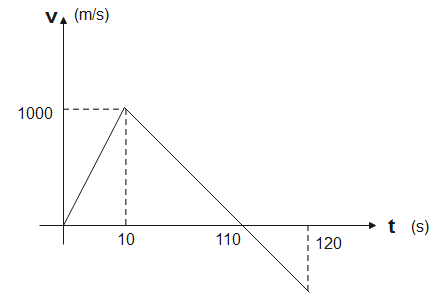
According to the graph, the rocket moves in one direction. After it attains maximum velocity in one direction its velocity decreases till it reaches zero and then starts increasing in the opposite direction.
The formula for velocity is given by-
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$ - (1)
It reaches maximum velocity at the moment it attains its maximum velocity.
So, it can reach the maximum height when all of its kinetic energy is converted to potential energy. At maximum height total energy of the body is equal to its potential energy
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mgh$ - (2)
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$ is the kinetic energy of the rocket
$mgh$ is the potential energy of the rocket
$m$ is the mass
$v$ is its velocity
$h$ is height above the Earth’s surface
$g$ is acceleration due to gravity
Substituting given values for rocket in eq (2), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}{{v}^{2}}=gh \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{{({{10}^{3}})}^{2}}=10\times h \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{10}^{5}}}{2}m=h \\
& \Rightarrow 5\times {{10}^{4}}m=h \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow 5\times {{10}^{4}}\times {{10}^{-3}}km=h$
$\therefore 50km=h$
Therefore, the maximum height attained by the rocket above the earth’s surface is $50km$.
Note:
As height increases, potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. The potential energy is highest at maximum height and kinetic energy is lowest. The mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic and potential energy and it remains constant throughout. As the rocket is moving against gravity, the gravitational pull of the earth does work on the rocket which is stored as its potential energy.
Formula Used:
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mgh$
Complete step-by-step solution:

Velocity is defined as the displacement covered in unit time. Its SI unit is $m{{s}^{-1}}$.
According to the graph, the rocket moves in one direction. After it attains maximum velocity in one direction its velocity decreases till it reaches zero and then starts increasing in the opposite direction.
The formula for velocity is given by-
$v=\dfrac{d}{t}$ - (1)
It reaches maximum velocity at the moment it attains its maximum velocity.
So, it can reach the maximum height when all of its kinetic energy is converted to potential energy. At maximum height total energy of the body is equal to its potential energy
$\therefore \dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}=mgh$ - (2)
$\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$ is the kinetic energy of the rocket
$mgh$ is the potential energy of the rocket
$m$ is the mass
$v$ is its velocity
$h$ is height above the Earth’s surface
$g$ is acceleration due to gravity
Substituting given values for rocket in eq (2), we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{2}{{v}^{2}}=gh \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{{({{10}^{3}})}^{2}}=10\times h \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{10}^{5}}}{2}m=h \\
& \Rightarrow 5\times {{10}^{4}}m=h \\
\end{align}$
$\Rightarrow 5\times {{10}^{4}}\times {{10}^{-3}}km=h$
$\therefore 50km=h$
Therefore, the maximum height attained by the rocket above the earth’s surface is $50km$.
Note:
As height increases, potential energy increases and kinetic energy decreases. The potential energy is highest at maximum height and kinetic energy is lowest. The mechanical energy is the sum of kinetic and potential energy and it remains constant throughout. As the rocket is moving against gravity, the gravitational pull of the earth does work on the rocket which is stored as its potential energy.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




