
Fructose and Glucose can be distinguished by
(A) Fehling’s test
(B) Barfoed’s test
(C) Benedict’s test
(D) Seliwanoff’s test
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: To determine the answer to this question we should know the structural difference between glucose and fructose and we should also know the reactivity of the given test. Glucose and Fructose are monosaccharides. Their molecular formula is the same i.e., ${{\text{C}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{12}}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{6}}}$ but the functional groups are different i.e., glucose contains $ - {\text{CHO}}$ (aldehyde) group and fructose contains $ - {\text{C(O)}} - $ ketone group.
Complete answer:
Glucose and Fructose are structural isomers. Their structures are,
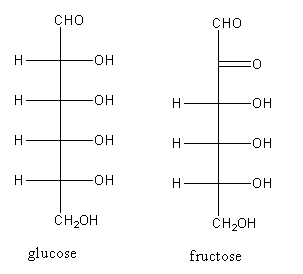
Both have carbonyl groups but glucose shows reducing property due to the presence of $ - {\text{CHO}}$ (aldehyde) while Fructose does not. Fehling solution is prepared by combining two solutions i.e, Fehling A and Fehling B. Fehling A is deep blue aq. Solution of copper (II) sulphate. Fehling B is a colourless solution of aq. potassium sodium tartrate with strong alkali such as sodium or potassium hydroxide.
When Fehling solution which is a deep blue solution of${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}$reacts with glucose, the copper (II) ions reduce to a red precipitate of insoluble copper oxide.
The reaction of glucose with Fehling solution is as follows:
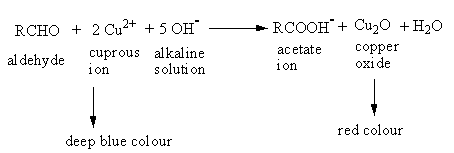
So, fructose and Glucose can be distinguished by Fehling’s test. Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct option is (A) Fehling’s test.
Additional Information:
i) Benedict reagent is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate and copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate. It is used to test for simple carbohydrates.
ii) Barfoed’s test is used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$ to ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{\text{ + }}}$ oxide which forms a brick-red precipitate.
iii) Sliwanoff’s test is a chemical test that distinguishes between aldose and ketose sugar.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: Fehling solution B is also known as Rochelle’s salt. As only aldehyde sugars get reduced by Fehling solution, In this test only the presence of aldehydes is detected, not the presence of ketones. Fehling solution is a reducing agent of aliphatic aldehydes. Because glucose is a reducing sugar it can also be detected by Tollen, Fehling, and Baeyer and Benedict reagent. The sugars that have a free carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone) are known as reducing sugars such as glucose. All monosaccharides are reducing sugar
Complete answer:
Glucose and Fructose are structural isomers. Their structures are,

Both have carbonyl groups but glucose shows reducing property due to the presence of $ - {\text{CHO}}$ (aldehyde) while Fructose does not. Fehling solution is prepared by combining two solutions i.e, Fehling A and Fehling B. Fehling A is deep blue aq. Solution of copper (II) sulphate. Fehling B is a colourless solution of aq. potassium sodium tartrate with strong alkali such as sodium or potassium hydroxide.
When Fehling solution which is a deep blue solution of${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{2 + }}$reacts with glucose, the copper (II) ions reduce to a red precipitate of insoluble copper oxide.
The reaction of glucose with Fehling solution is as follows:

So, fructose and Glucose can be distinguished by Fehling’s test. Therefore, from the above explanation, the correct option is (A) Fehling’s test.
Additional Information:
i) Benedict reagent is a mixture of sodium carbonate, sodium citrate and copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate. It is used to test for simple carbohydrates.
ii) Barfoed’s test is used for detecting the presence of monosaccharides. It is based on the reduction of ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{{\text{2 + }}}}$ to ${\text{C}}{{\text{u}}^{\text{ + }}}$ oxide which forms a brick-red precipitate.
iii) Sliwanoff’s test is a chemical test that distinguishes between aldose and ketose sugar.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: Fehling solution B is also known as Rochelle’s salt. As only aldehyde sugars get reduced by Fehling solution, In this test only the presence of aldehydes is detected, not the presence of ketones. Fehling solution is a reducing agent of aliphatic aldehydes. Because glucose is a reducing sugar it can also be detected by Tollen, Fehling, and Baeyer and Benedict reagent. The sugars that have a free carbonyl group (aldehyde or ketone) are known as reducing sugars such as glucose. All monosaccharides are reducing sugar
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




