
Fruit of peanut is
(a) Pod
(b) Achene
(c) Caryopsis
(d) Drupe
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: These are the fruit of plants in the pea family (Fabaceae) . Most legumes are dehiscent fruits that release their seeds by splitting open along two seams, though some, such as peanuts (Arachis hypogaea) and carobs (Ceratonia siliqua) , do not naturally open.
Correct step by step answer:
A. Pods develop underground, an unusual feature referred to as geocarpy. After fertilization, a brief stalk at the bottom of the ovary (termed a pedicel) elongates to make a thread-like structure referred to as a "peg". This peg grows down into the soil, and therefore the tip, which contains the ovary, develops into a mature peanut pod.
B. Achene- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is tough, leathery and remains free from testa. E.g. Mirabilis.
C. Caryopsis- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is fused with the testa. E.g. Wheat.
D. Drupe- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is differentiated into outer, thin epicarp, middle fleshy and fibrous mesocarp and inner hard and stony endocarp. E.g. Mango.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Pod.’
Additional Information: The seeds of both peas and castor are dicots while maize seeds are monocots. Within the seed of a plant, a cotyledon is a significant part of the embryo. It is defined as the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants. Based on the number of cotyledons, botanists classify flowering plants (angiosperms) into :
a) plants with one embryonic leaf, termed monocotyledonous (monocots).
b) plants with two embryonic leaves, termed dicotyledonous (dicots).
- In monocots, the cotyledon is called a scutellum which is directly connected to the embryo via vascular tissues xylem and phloem. Food reserves are stored in the large endosperm. Similarly in the dicots, the two cotyledons also have vascular connections to the embryo. In endospermic dicots, the food reserves are stored in endosperm. For example, tomato and pepper.
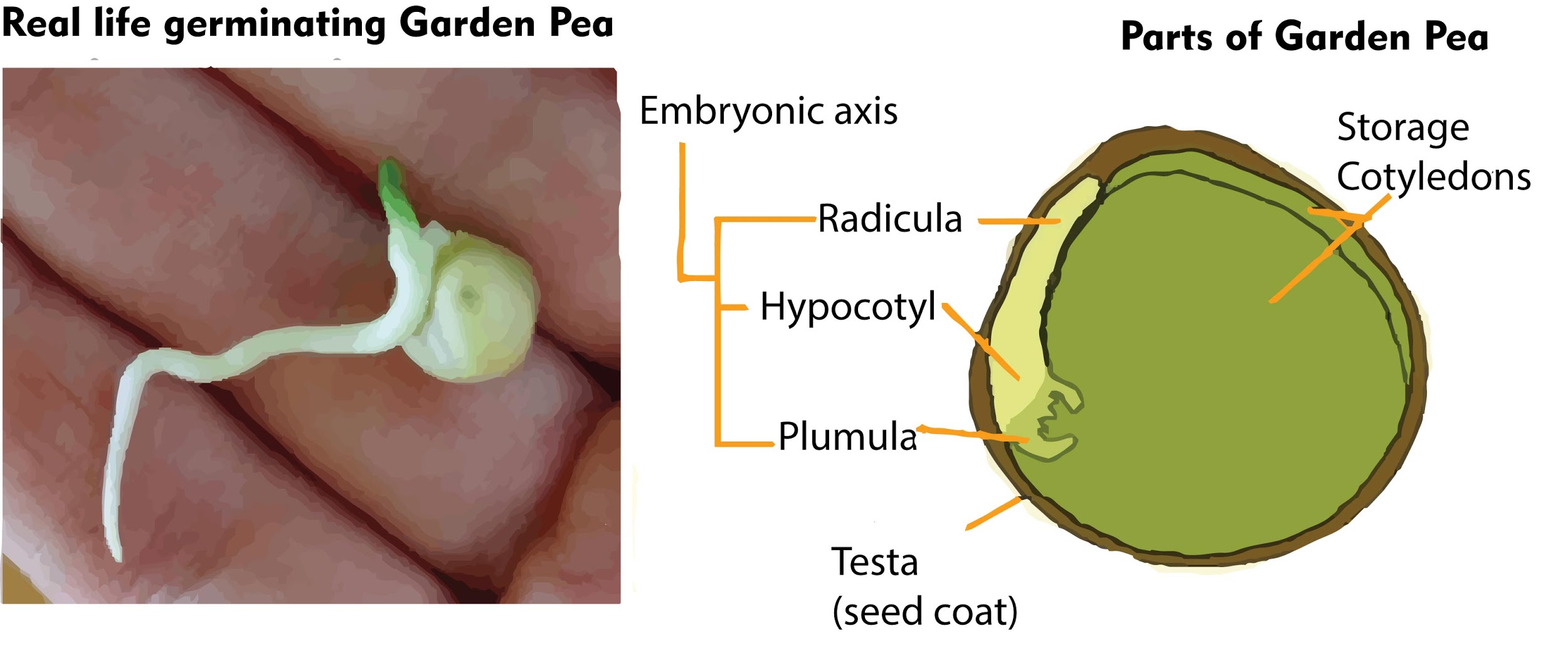
- In non-endospermic dicots, for example, split pea and peanuts, the triploid endosperm develops normally following double fertilization.
Note: Peanuts are as popular as they are healthy. They are an excellent plant-based source of protein and high in various vitamins, minerals, and also plant compounds. They are useful as a part of a weight loss diet and may reduce your risk of both heart disease and gallstones.
Correct step by step answer:
A. Pods develop underground, an unusual feature referred to as geocarpy. After fertilization, a brief stalk at the bottom of the ovary (termed a pedicel) elongates to make a thread-like structure referred to as a "peg". This peg grows down into the soil, and therefore the tip, which contains the ovary, develops into a mature peanut pod.
B. Achene- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is tough, leathery and remains free from testa. E.g. Mirabilis.
C. Caryopsis- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is fused with the testa. E.g. Wheat.
D. Drupe- a little, indehiscent, one-seeded fruit developing from a monocarpellary ovary and during which pericarp is differentiated into outer, thin epicarp, middle fleshy and fibrous mesocarp and inner hard and stony endocarp. E.g. Mango.

So, the correct answer is, ‘Pod.’
Additional Information: The seeds of both peas and castor are dicots while maize seeds are monocots. Within the seed of a plant, a cotyledon is a significant part of the embryo. It is defined as the embryonic leaf in seed-bearing plants. Based on the number of cotyledons, botanists classify flowering plants (angiosperms) into :
a) plants with one embryonic leaf, termed monocotyledonous (monocots).
b) plants with two embryonic leaves, termed dicotyledonous (dicots).
- In monocots, the cotyledon is called a scutellum which is directly connected to the embryo via vascular tissues xylem and phloem. Food reserves are stored in the large endosperm. Similarly in the dicots, the two cotyledons also have vascular connections to the embryo. In endospermic dicots, the food reserves are stored in endosperm. For example, tomato and pepper.
- In non-endospermic dicots, for example, split pea and peanuts, the triploid endosperm develops normally following double fertilization.
Note: Peanuts are as popular as they are healthy. They are an excellent plant-based source of protein and high in various vitamins, minerals, and also plant compounds. They are useful as a part of a weight loss diet and may reduce your risk of both heart disease and gallstones.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




